Cisco Spaces Captive Portal Runbook
CISCO VALIDATED
OVERVIEW
With the standard expectation of users to always be connected to the internet no matter where they are, it is paramount that users can be connected securely and seamlessly.
This Cisco validated runbook will look at Captive Portals to onboard customers.
A captive portal is the first touchpoint with your business for customers on Wi-Fi. It provides an opportunity to engage with customers who connect to Wi-Fi, offer relevant information, drive monetization, and potentially acquire customer information. Captive portals enable businesses to choose from multiple authentication mechanisms and deliver targeted experiences based on business rules. They can recognize repeat visitors and deliver customized offers, enhancing customer engagement and loyalty.
SUPPORT AND ONBOARDING
Please follow the link below to find out about the different ways to get support for Cisco Spaces.
PREREQUISITES
This Cisco validated runbook is designed only as a follow on from the Spaces OS Runbook. If you have not completed that runbook yet, please go back and ensure that the deployment has been validated against that before continuing here.
General Prerequisites
Captive Portal requires the following prerequisites met:
An active Cisco Spaces account.
A Cisco wireless network. Both controller-based (Cisco AireOS or Cisco Catalyst wireless controller) and cloud-based (Cisco Meraki) networks are supported.
Add the wireless network to your Cisco Spaces account.
For controller-based architecture, the Cisco Spaces Connector must be used.
For Cisco Meraki networks, add the Cisco Meraki account to your Cisco Spaces account.
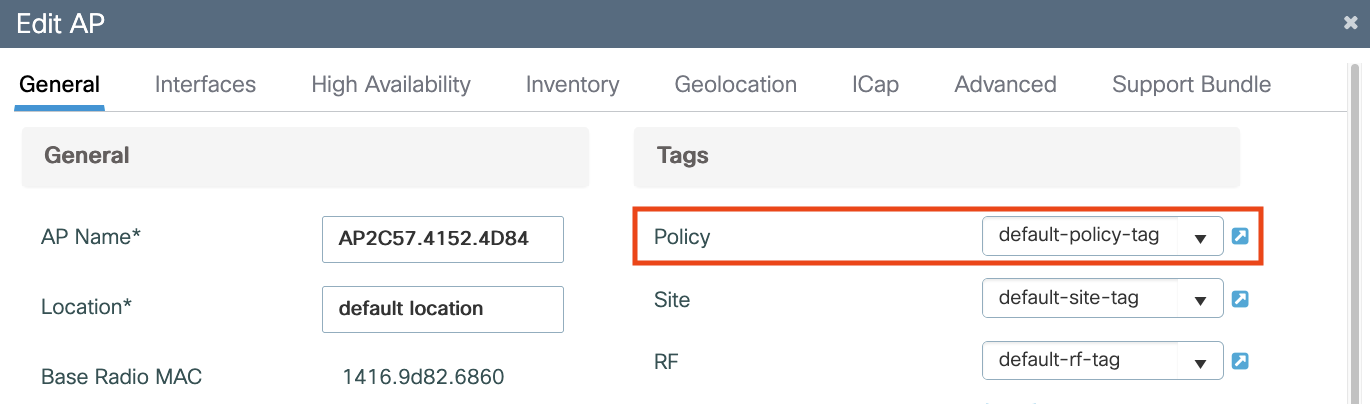
Wireless Access Points (WAPs) must be in the Cisco Spaces Location Hierarchy. If importing from Catalyst Centre, ensure that WAPs are assigned to floor maps in Catalyst Centre (not just to sites). This is a pre-requisitve to have the WAPs present in Cisco Spaces Location Hierarchy. Without WAPs being present in the Location Hierarchy, clients will not get redirected to the Captive Portal.
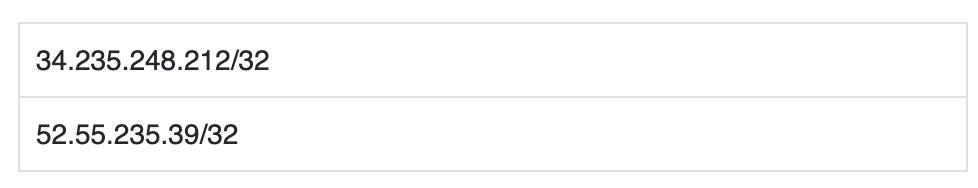
Captive Portal Firewall Port List and Routing
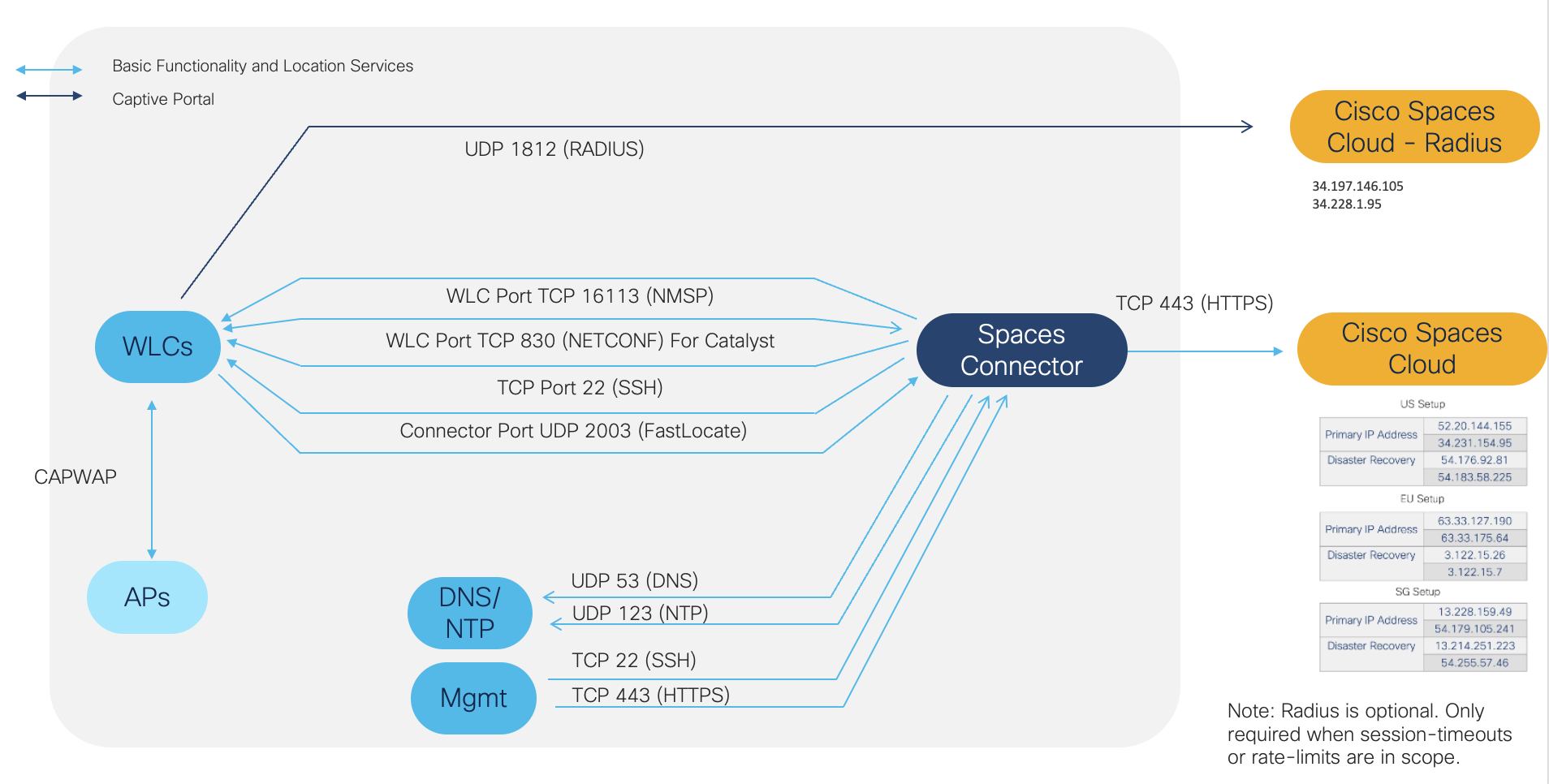
IMPLEMENTATION
At a hight level, the Cisco Spaces' Captive Portal architecture is as follows:
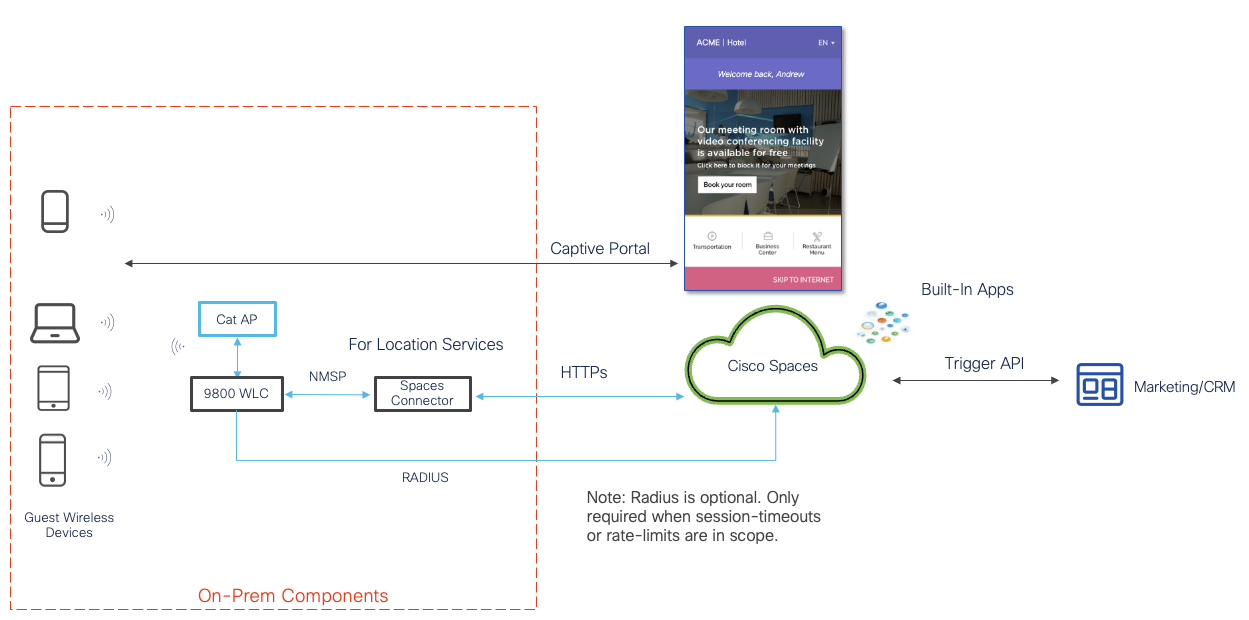
The process of setting up a Captive Portal requires two important tasks of i) Wireless Infrastructure Configuration and subsequently, ii) Captive Portal Configuration.
The Wireless Infrastructure Configuration ensures the underlying network is ready to host a Captive Portal setup. Once the Wireless Infrastructure configuration has been completed, the Captive Portal Configuration steps can commence on Cisco Spaces dashboard.
Wireless Infrastructure Configuration
Setting up Wireless Infrastructure for Captive Portal requires the following steps:
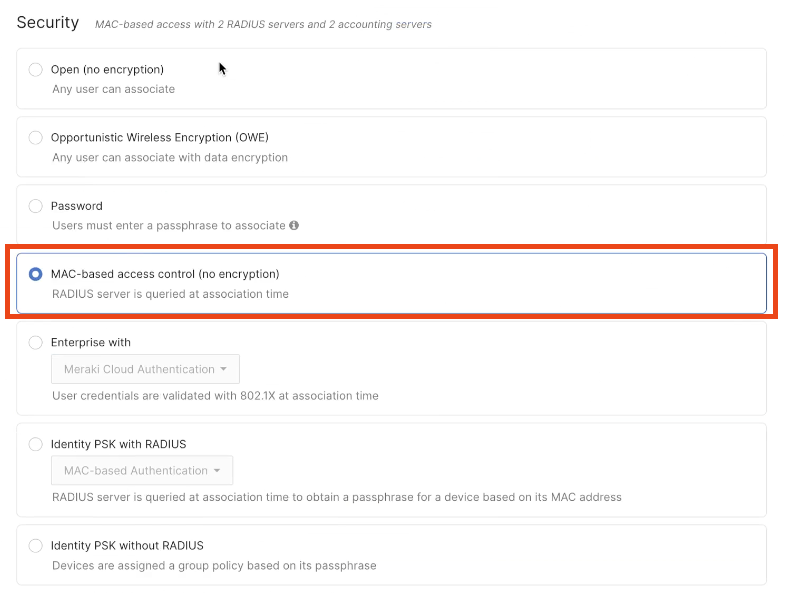
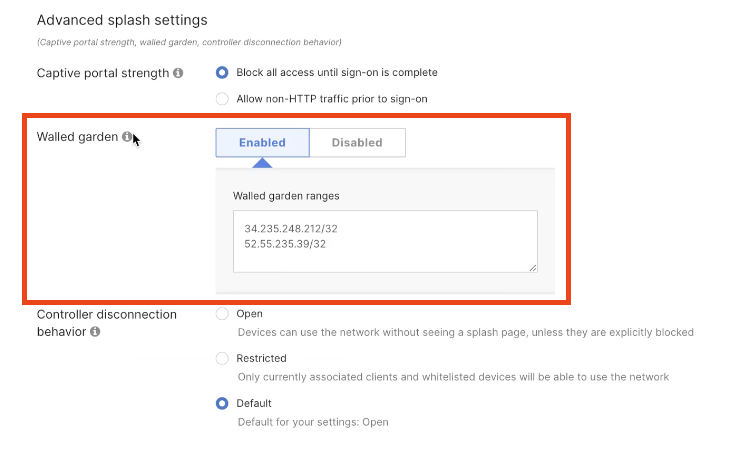
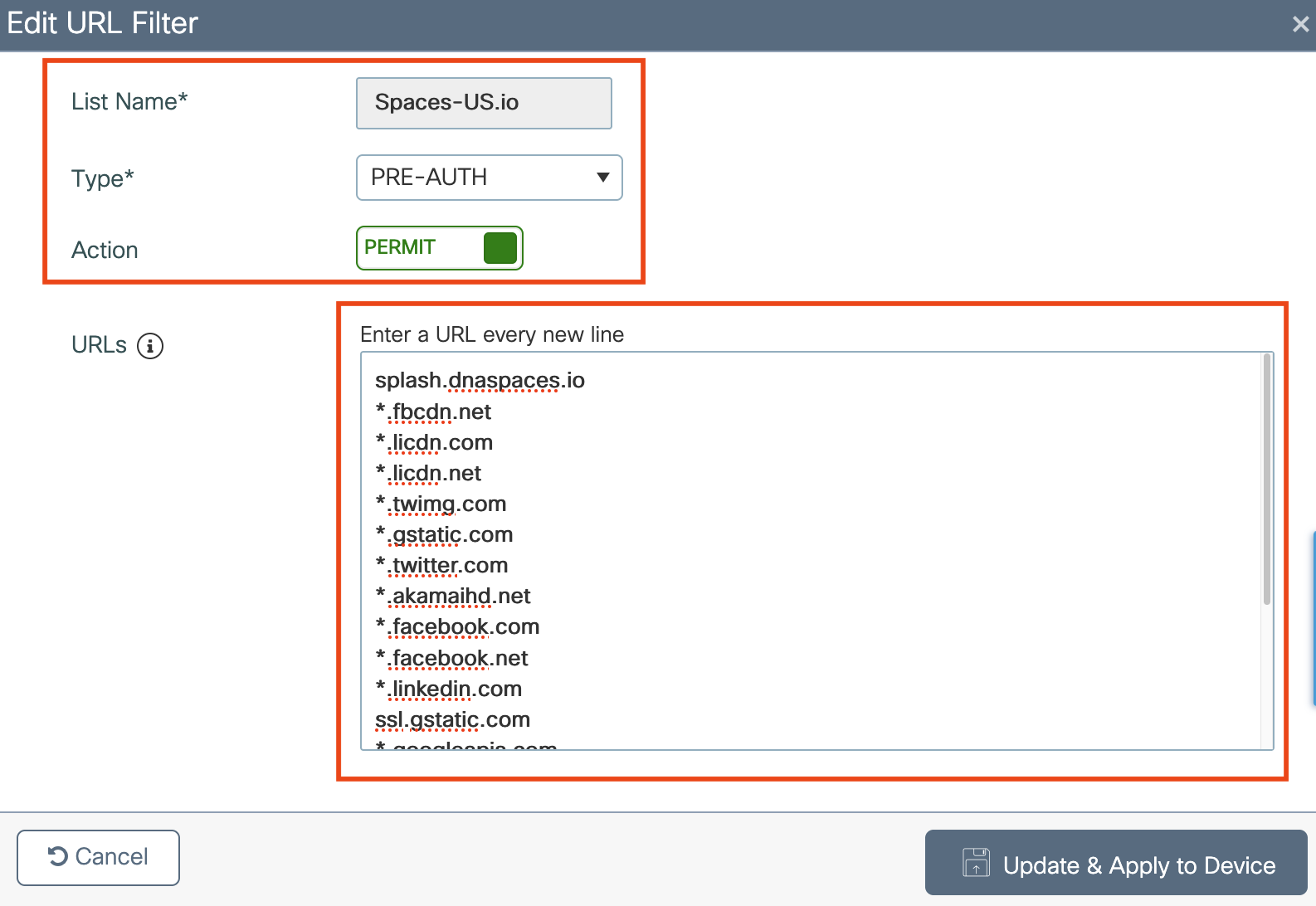
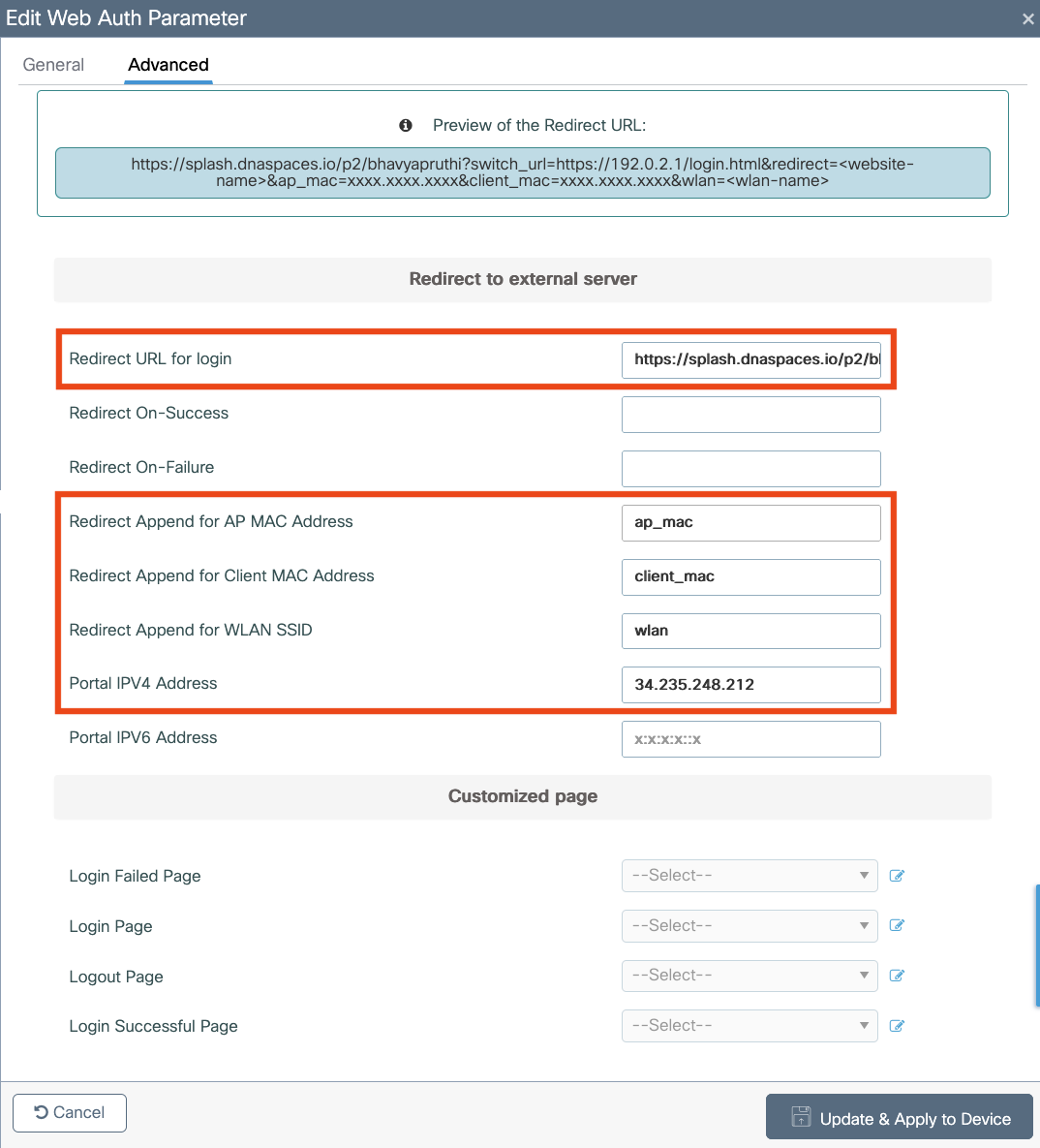
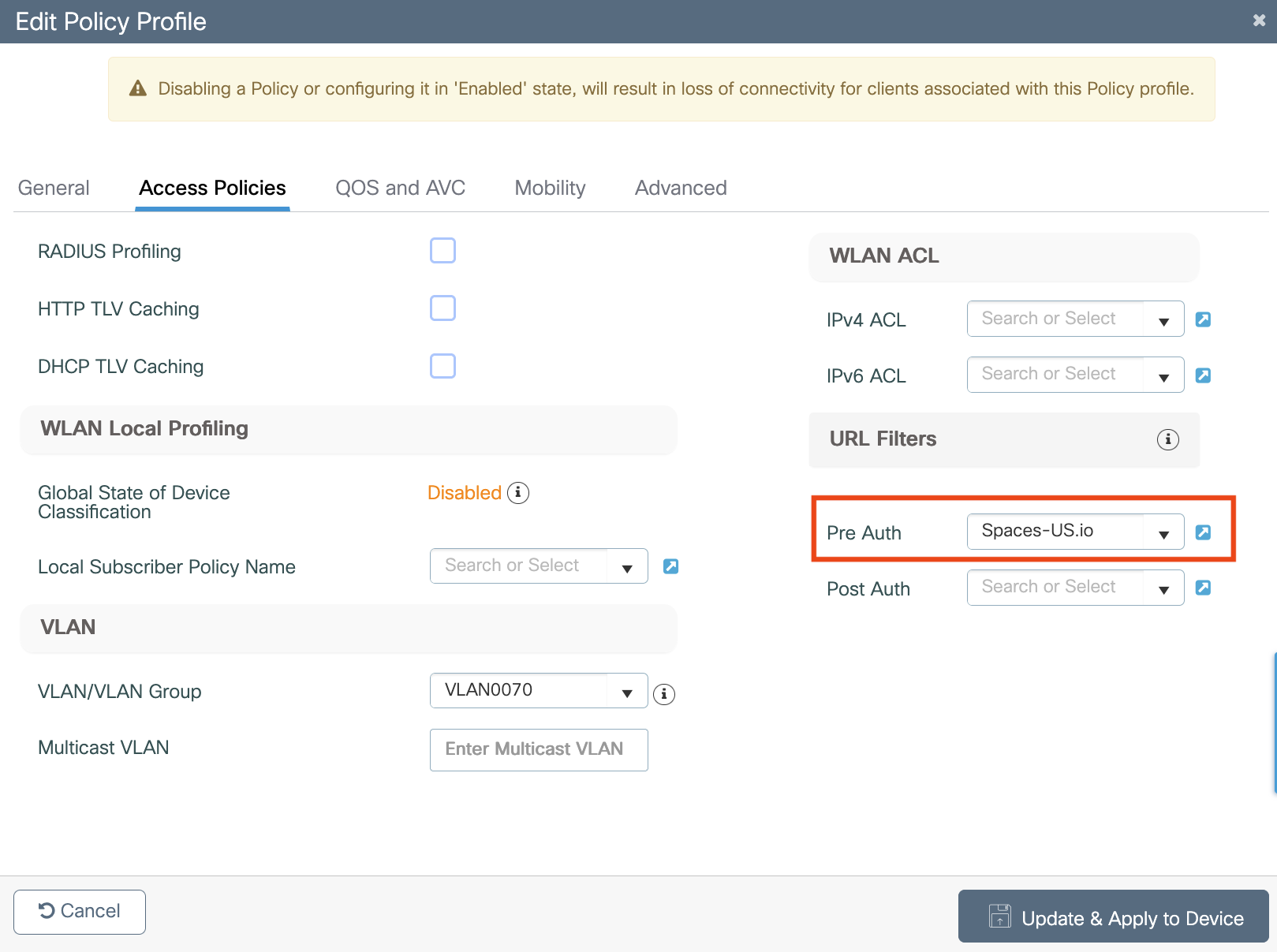
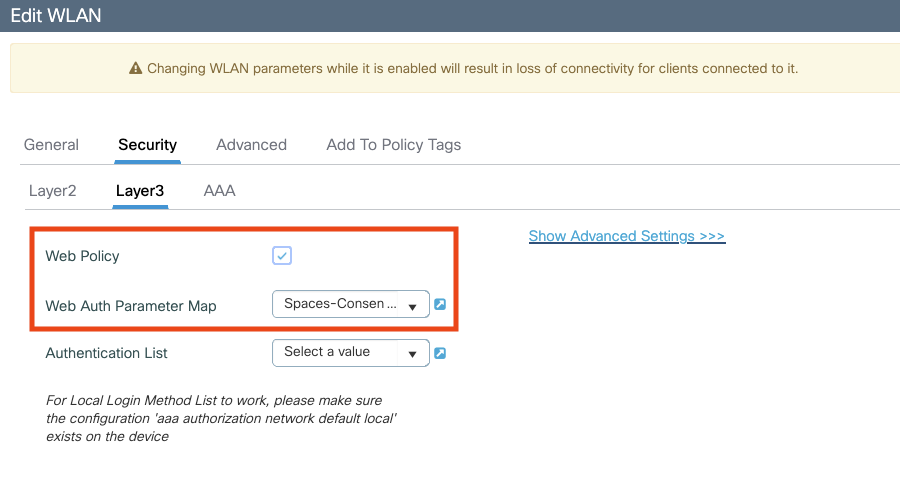
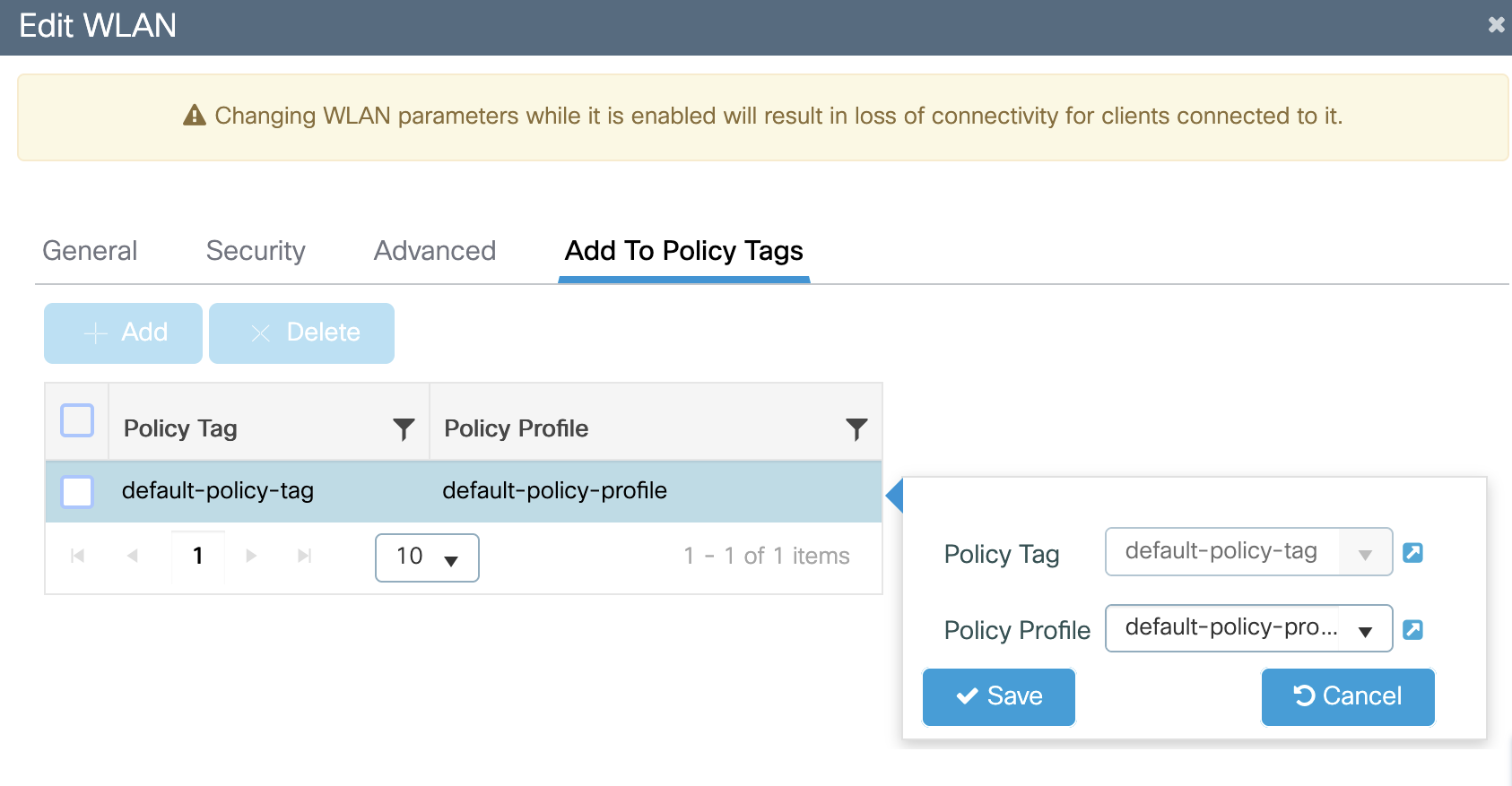
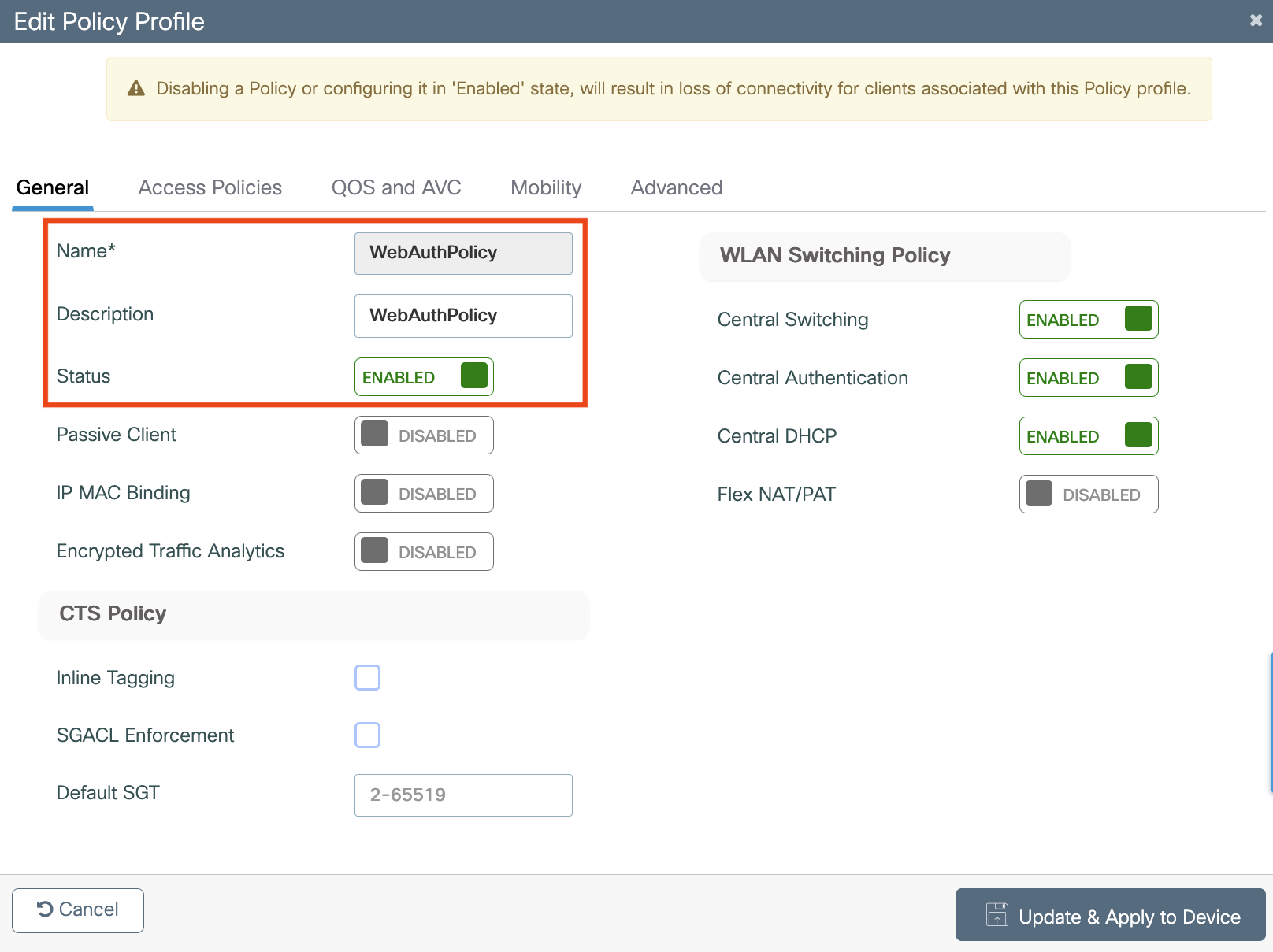
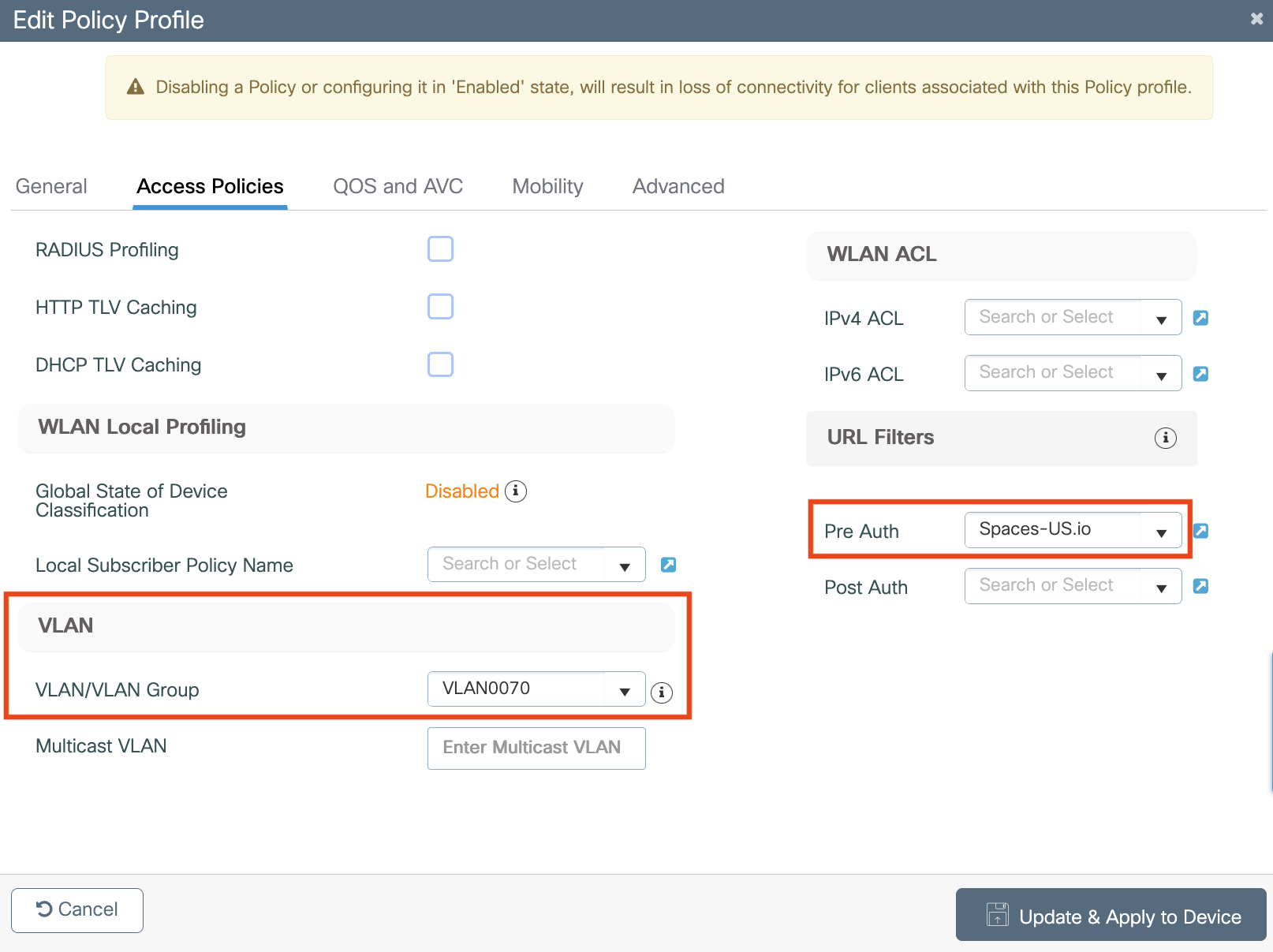
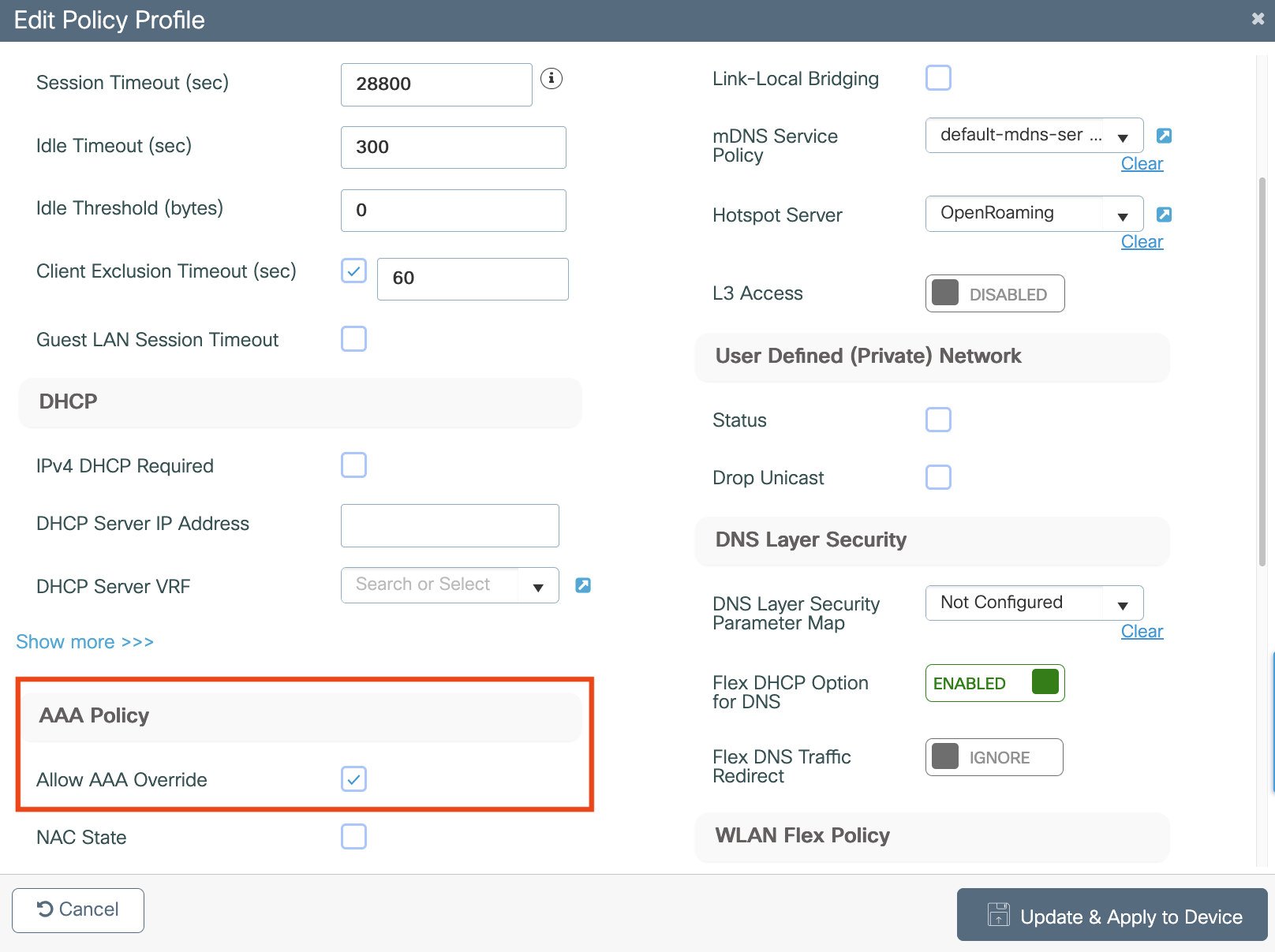
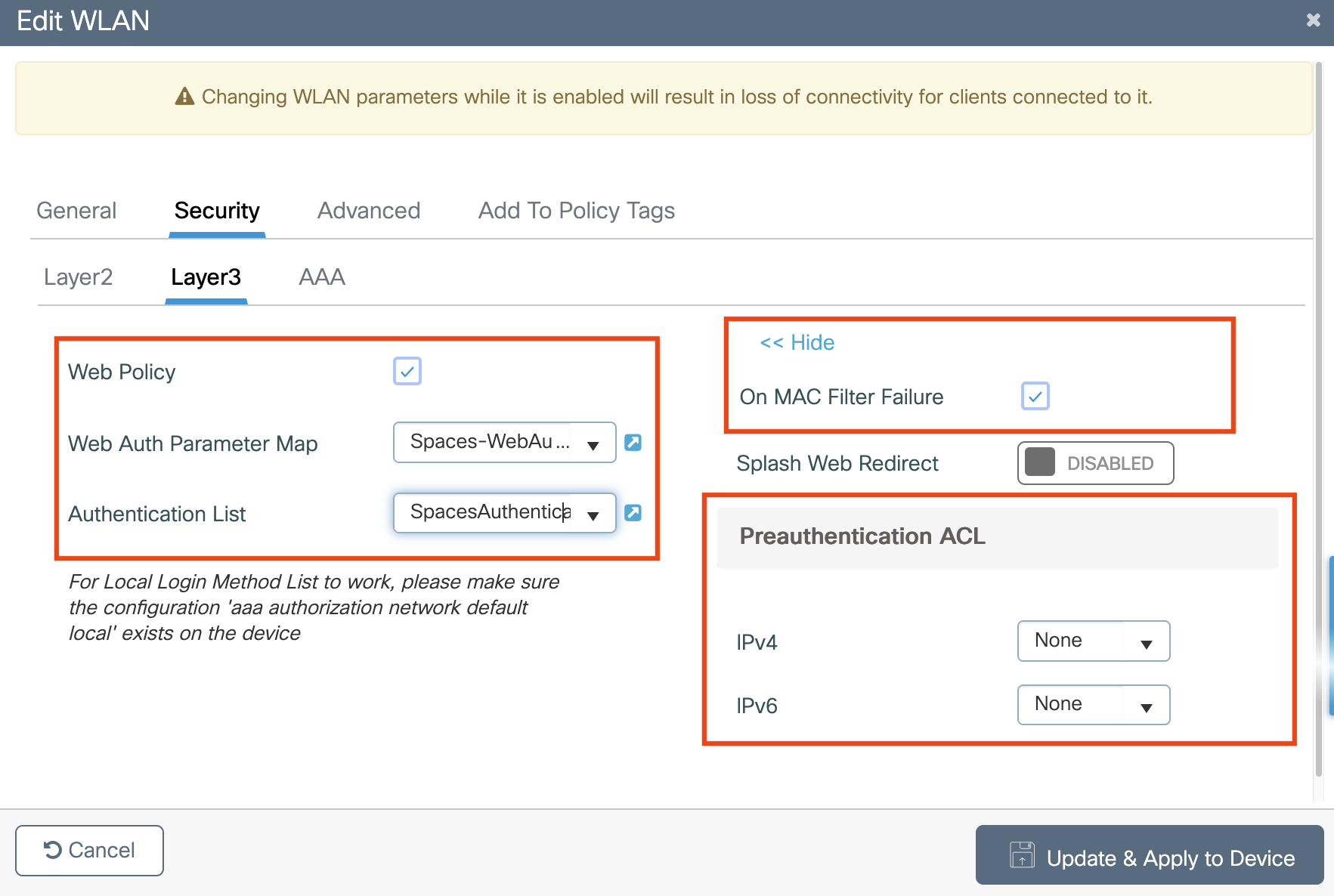
Configure webauths parameters
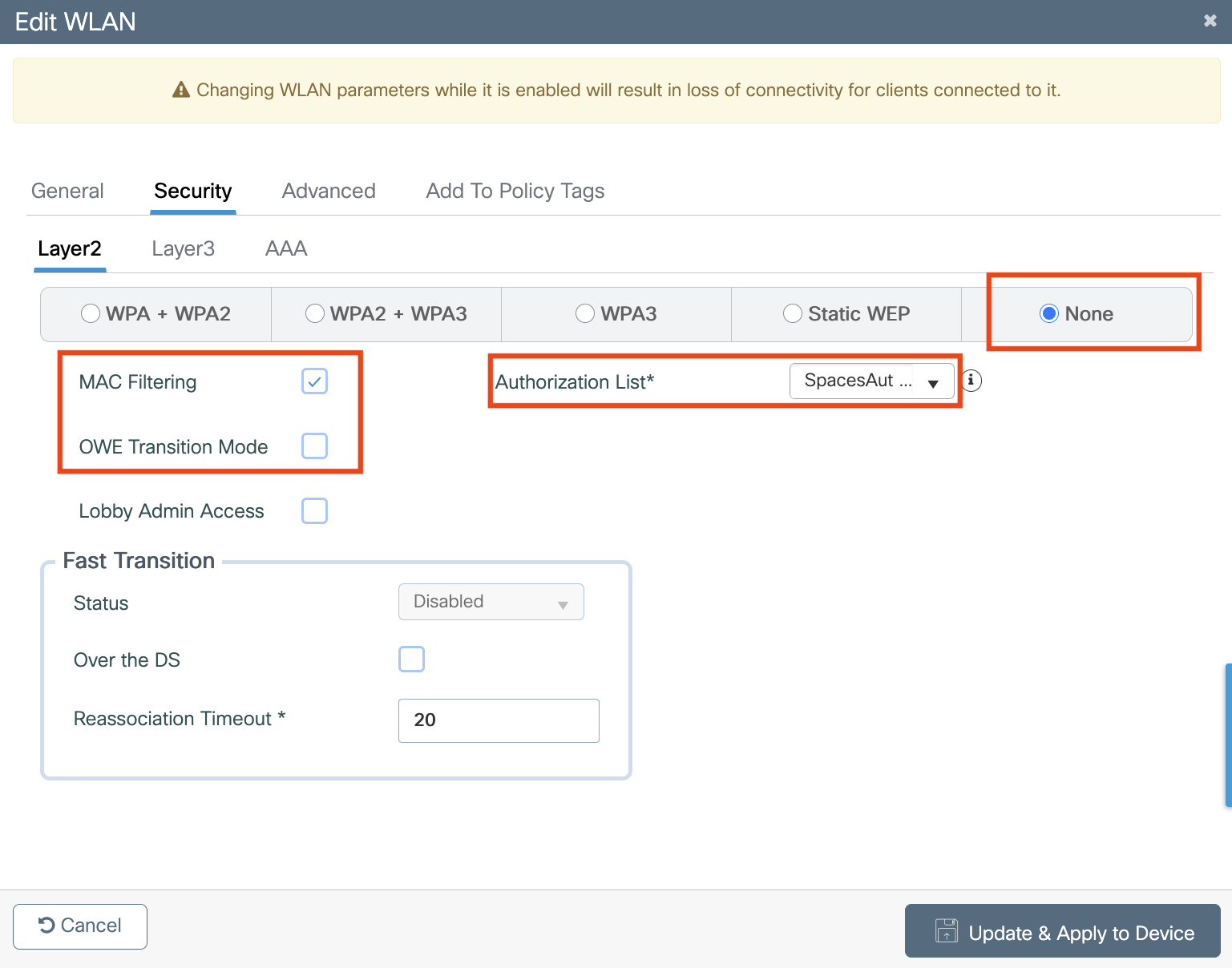
Configure ACLs
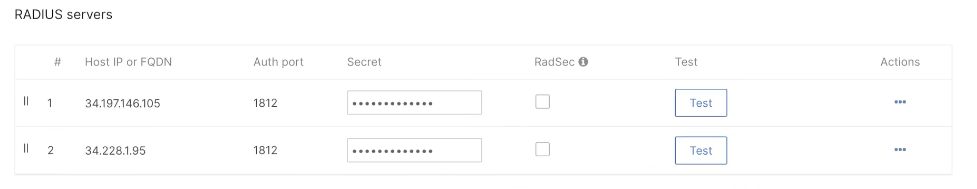
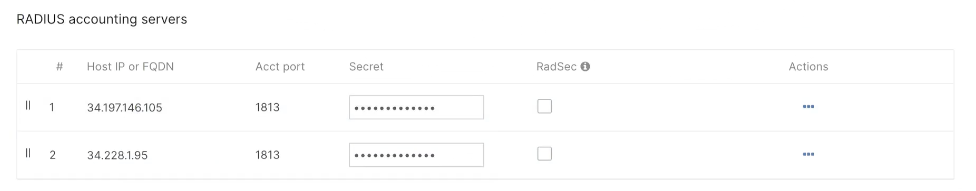
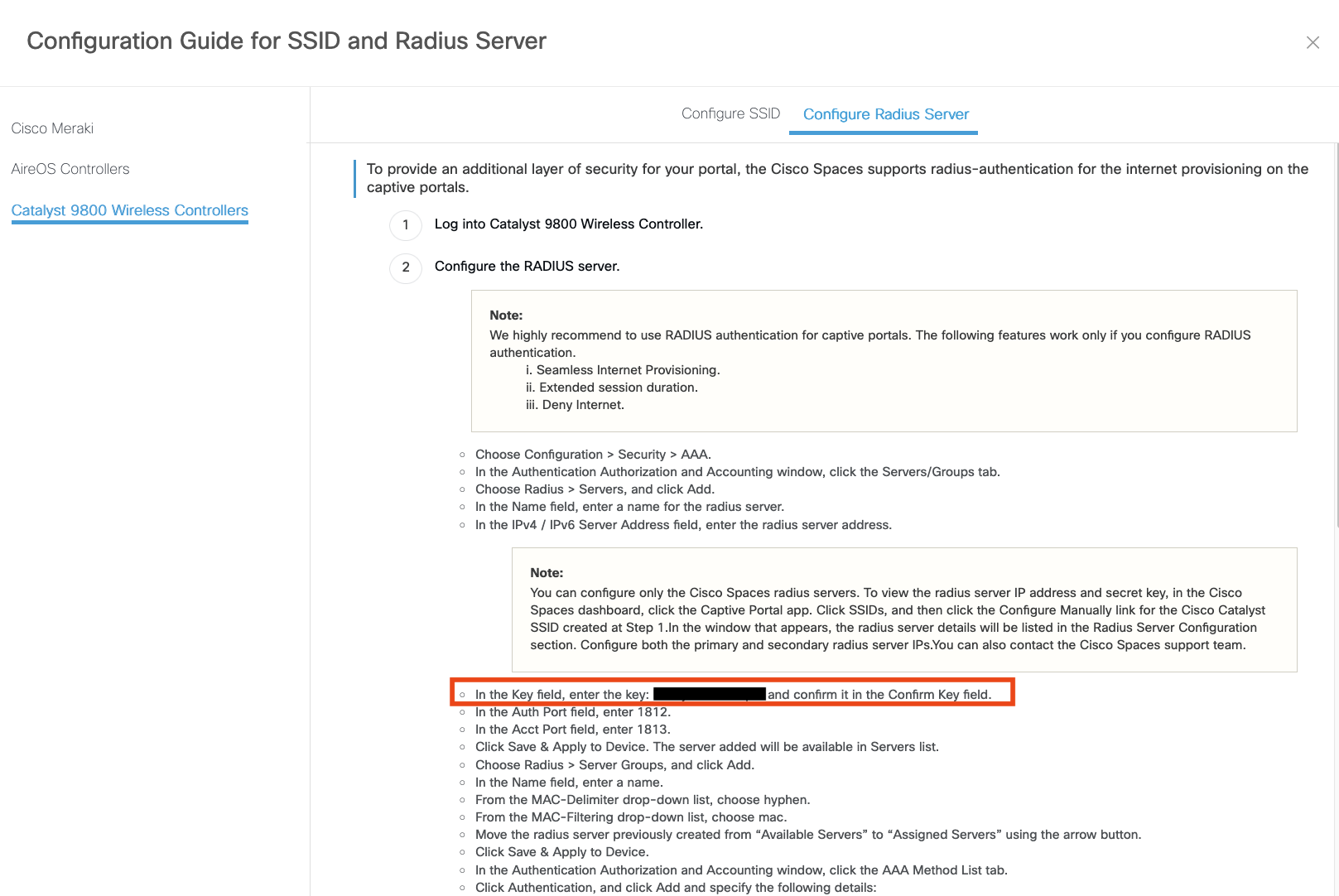
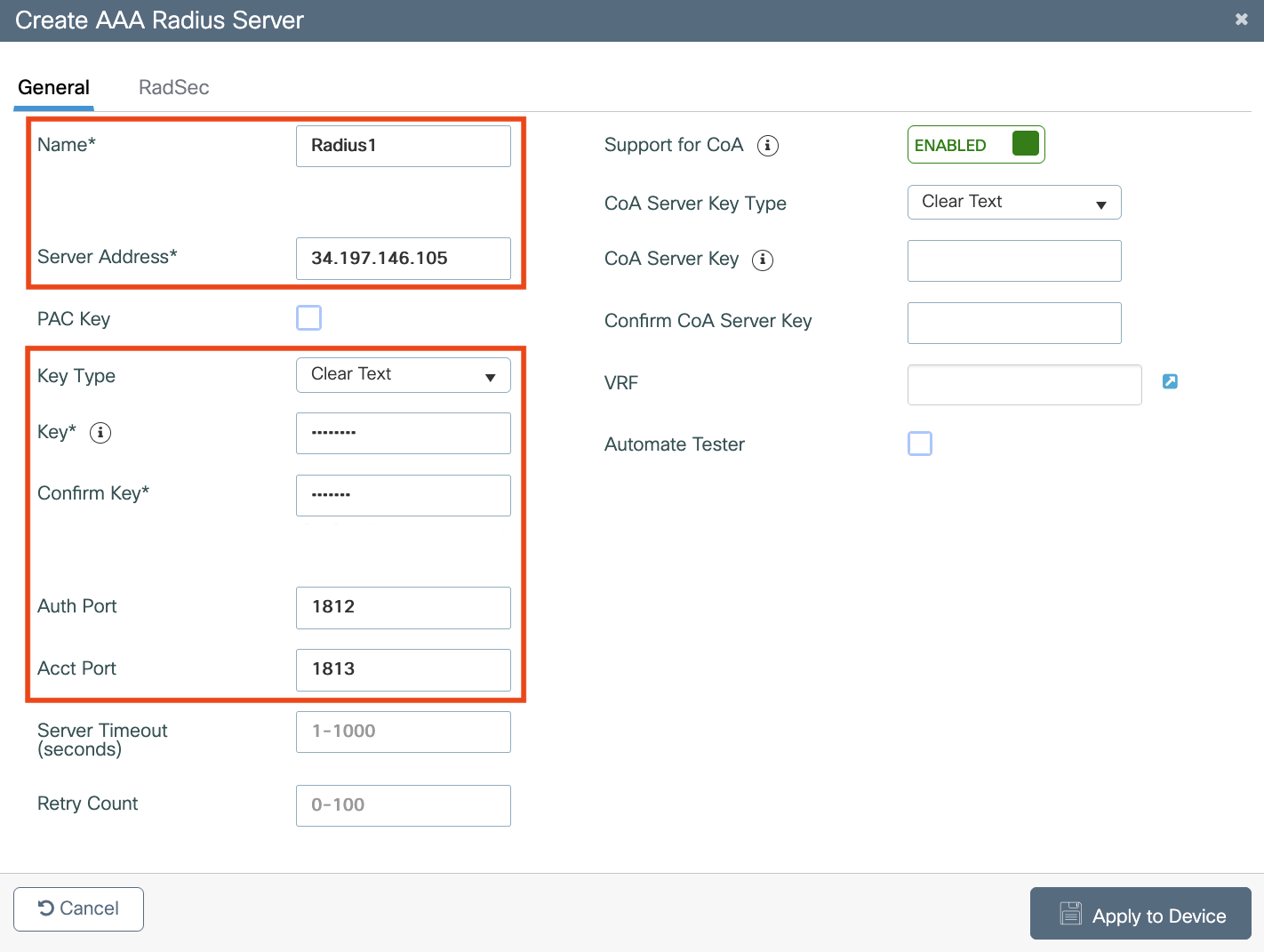
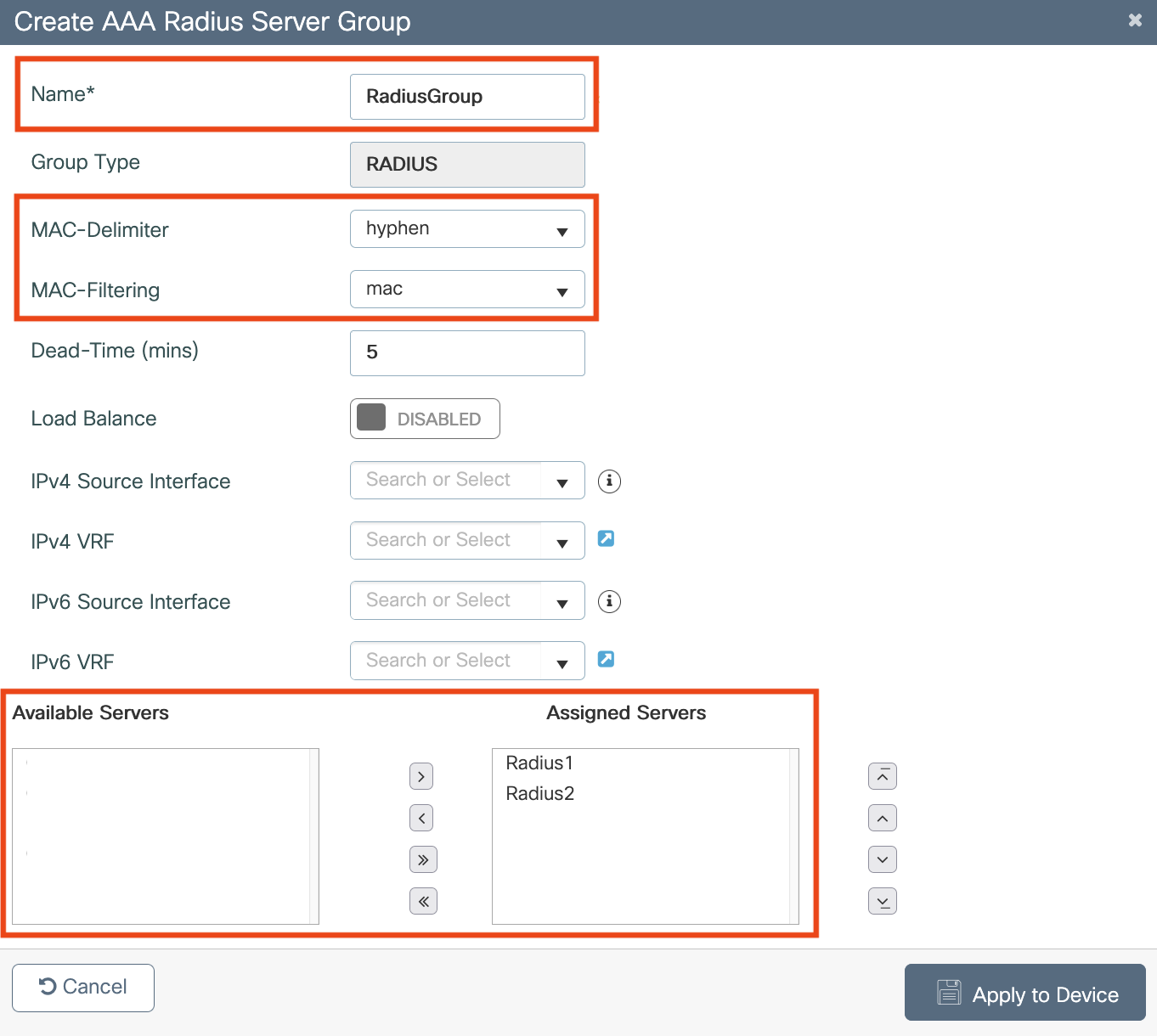
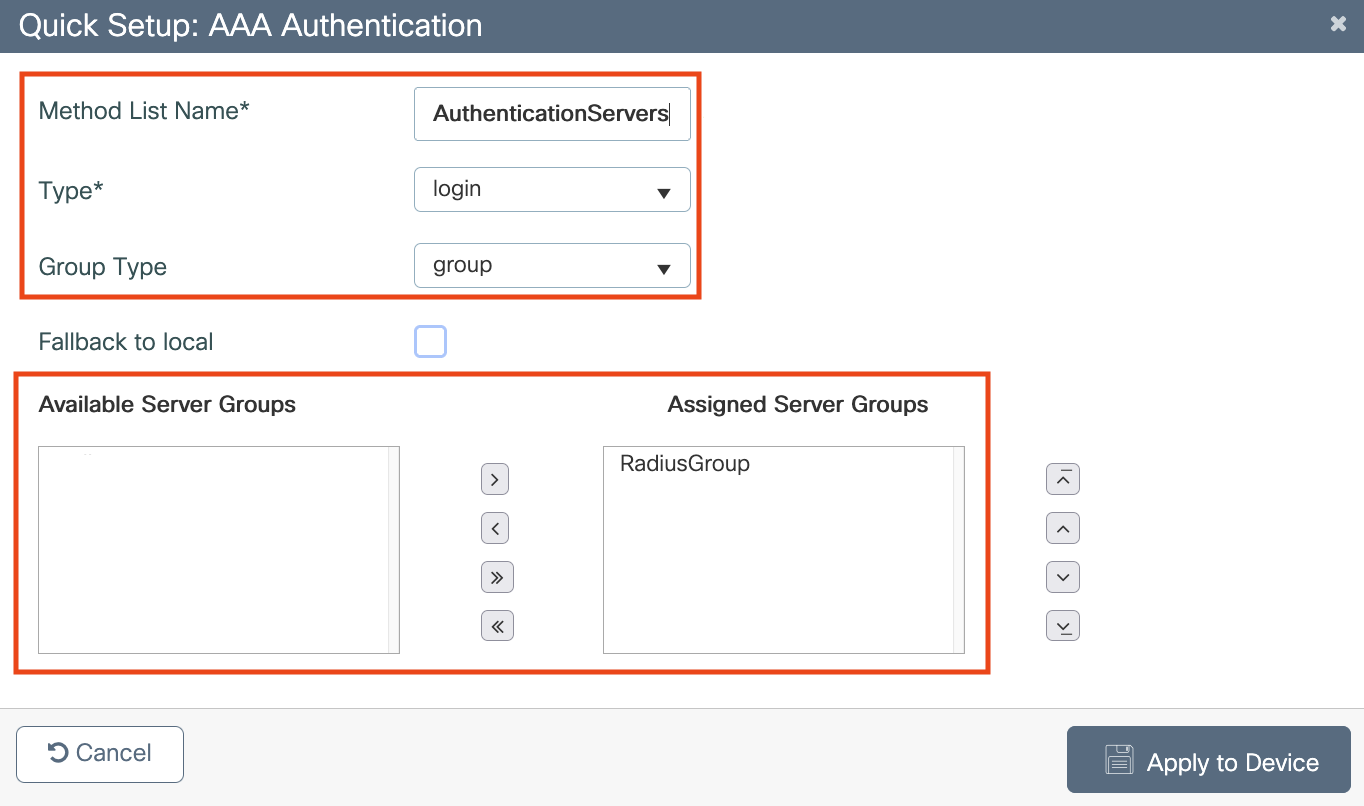
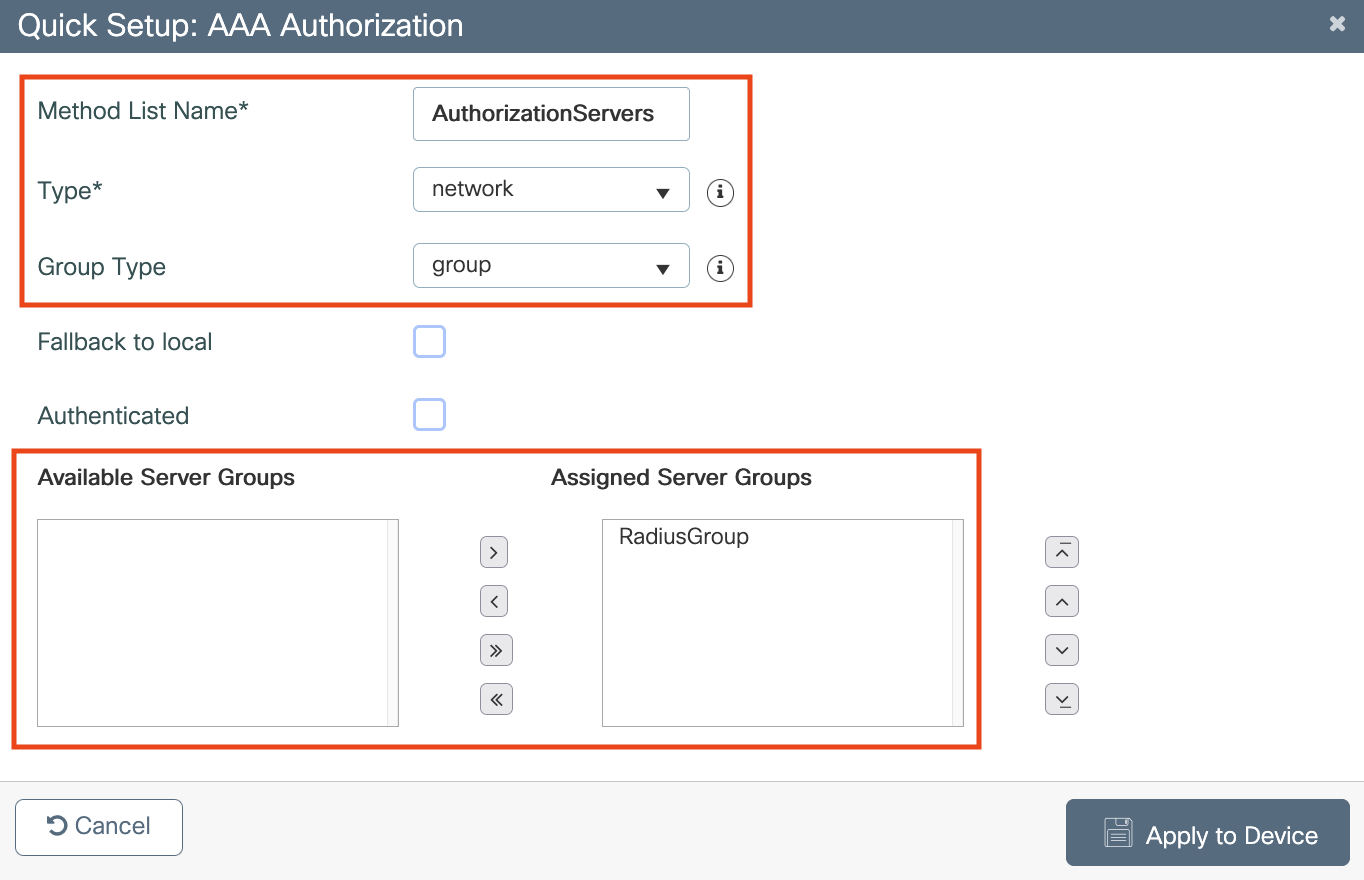
Configure AAA servers
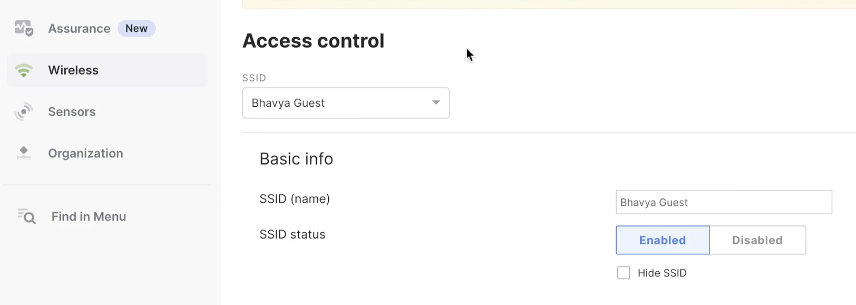
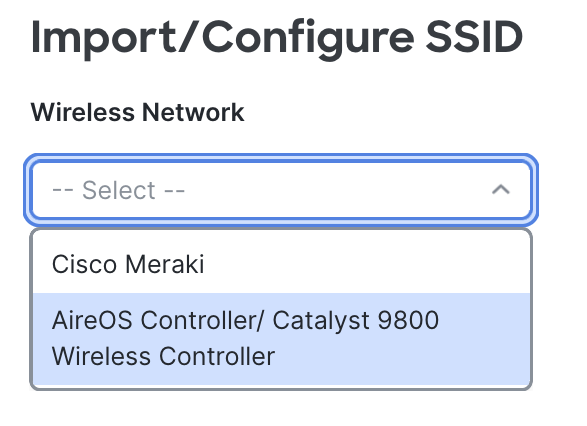
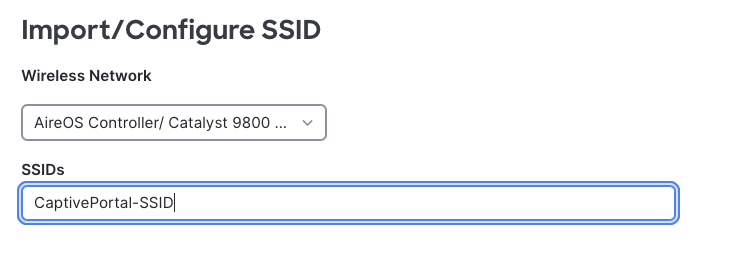
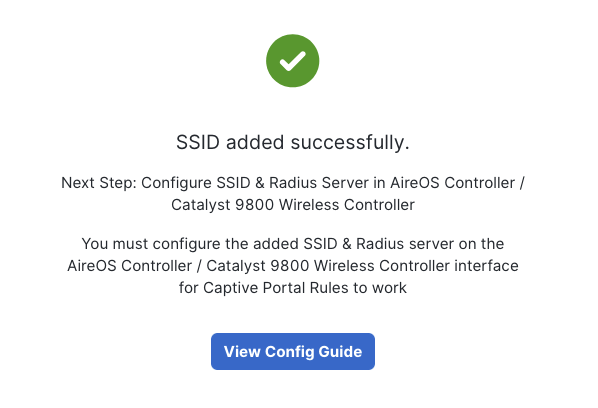
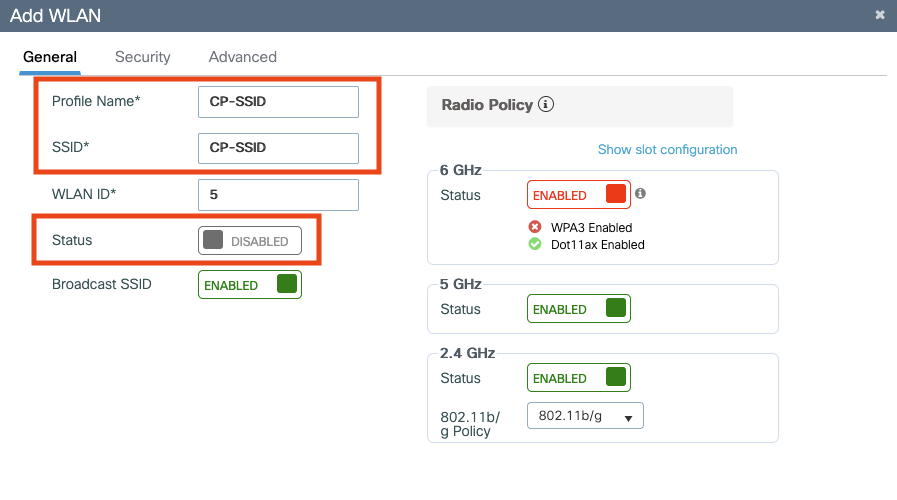
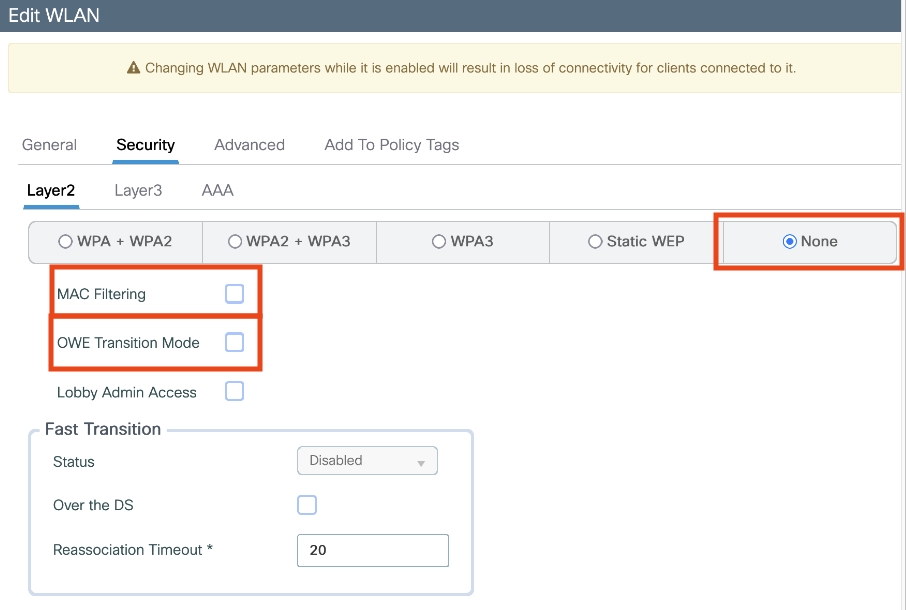
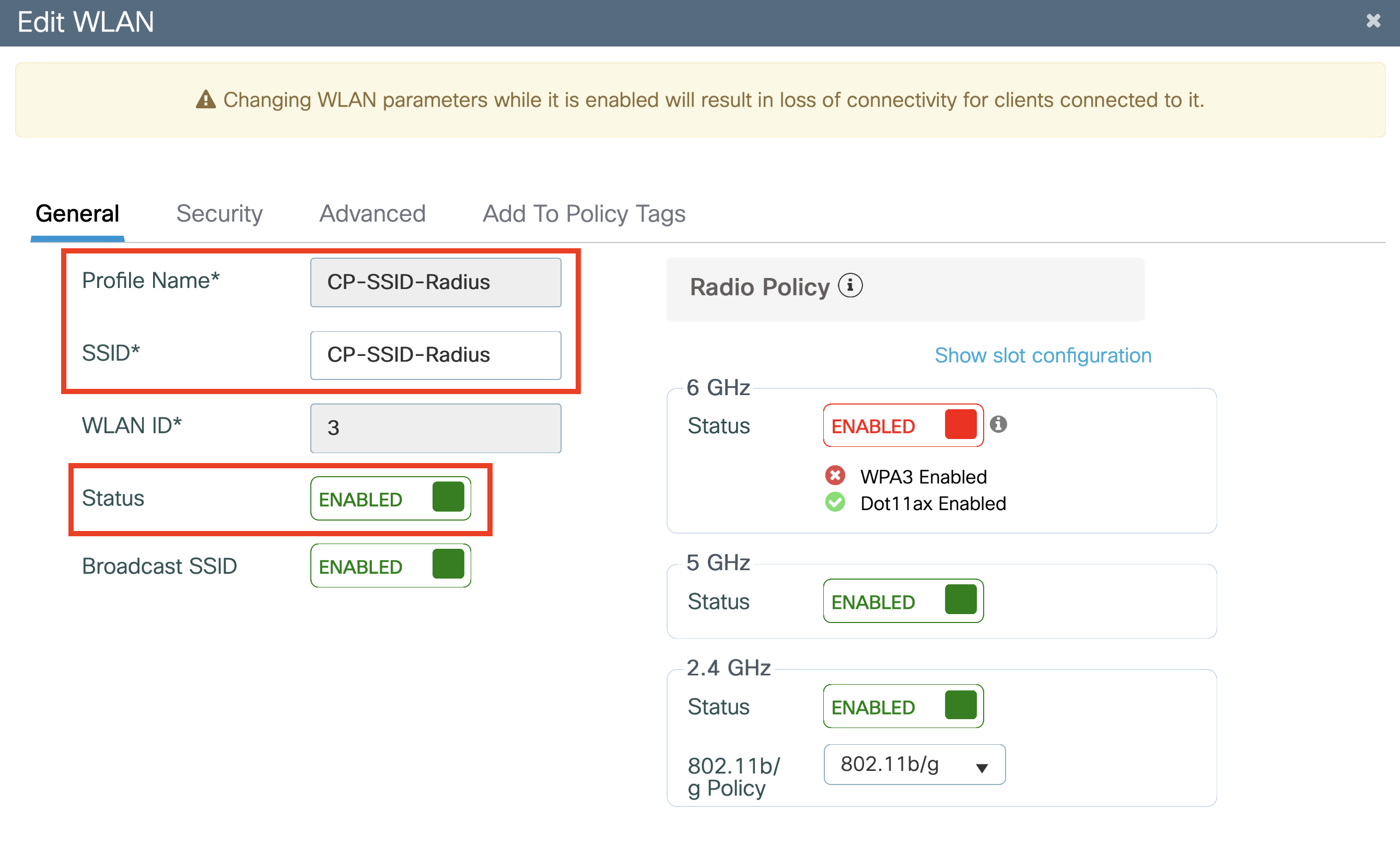
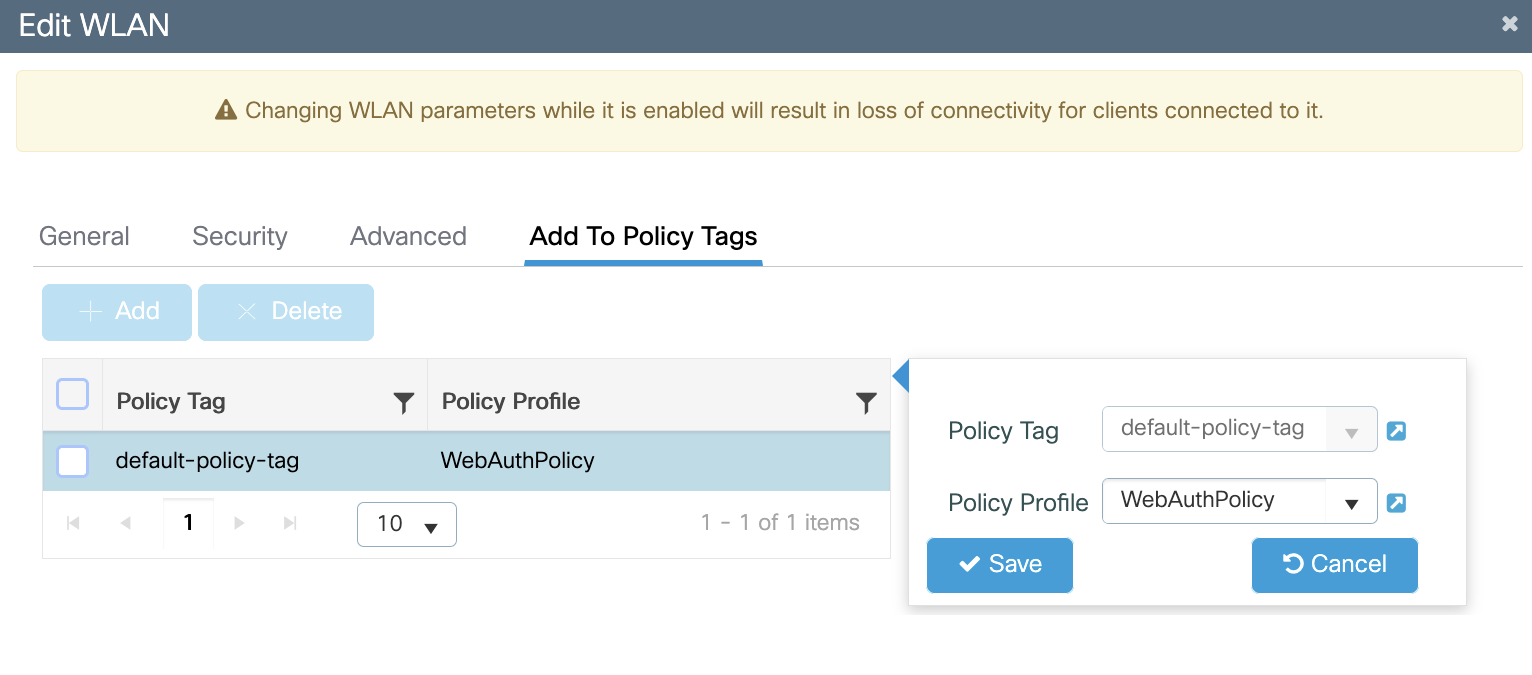
Configure SSID
Please refer to the relevant Wireless Infrastructure instructions based on the controller in your network.
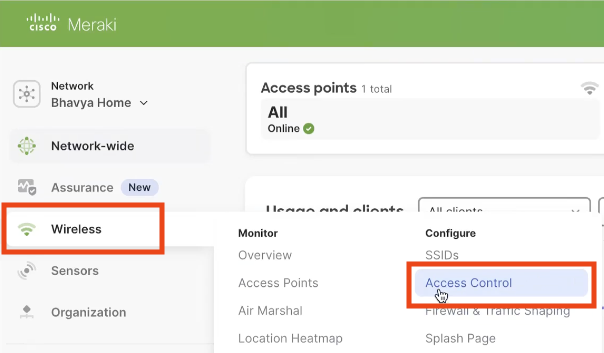
Meraki Wireless Infrastructure Configuration
Click the arrow to expand content related to Meraki Wireless Infrastructure Configuration.
Catalyst Wireless Infrastructure Configuration
Click the arrow to expand content related to Catalyst Wireless Infrastructure Configuration.
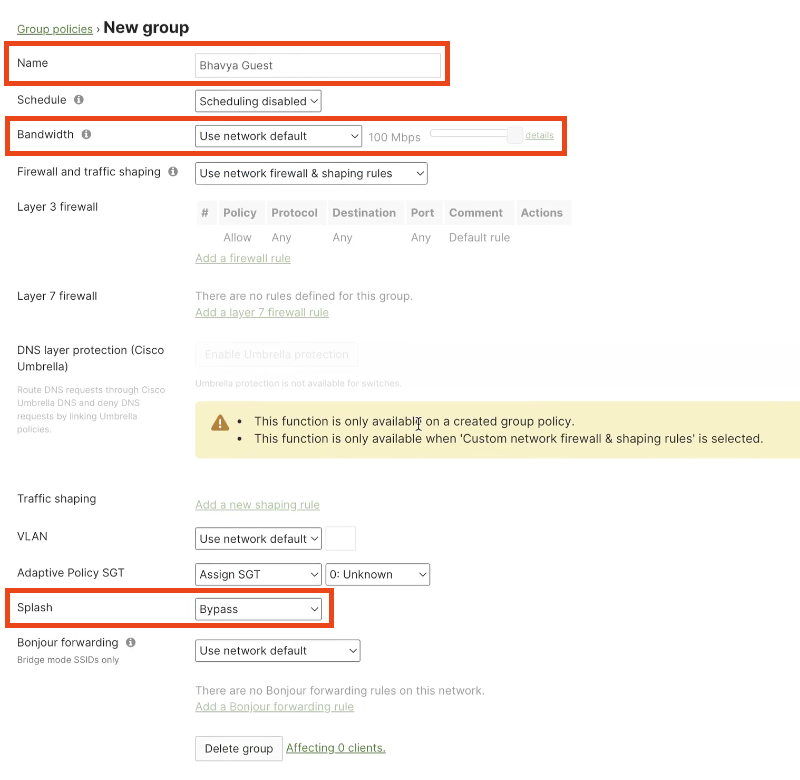
Captive Portal Configuration (No Authentication)
Once the Wireless Infrastructure has been setup. Configuring the Captivate Portal requires the following tasks:
Create or Import Portal
Set authentication and data capture settings
Configure rules and triggers
For a video guided demo, please see the links below:
How to Configure Captive Portal Rules
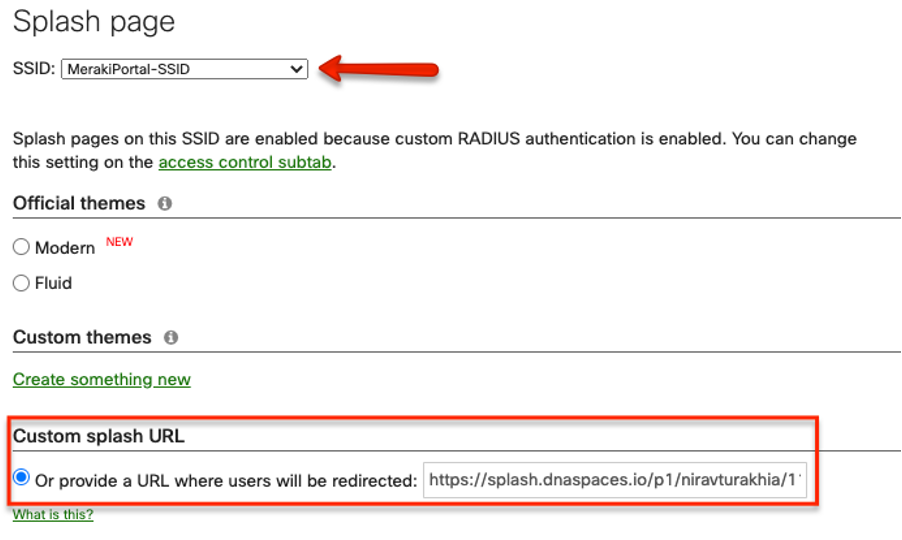
Create a Portal
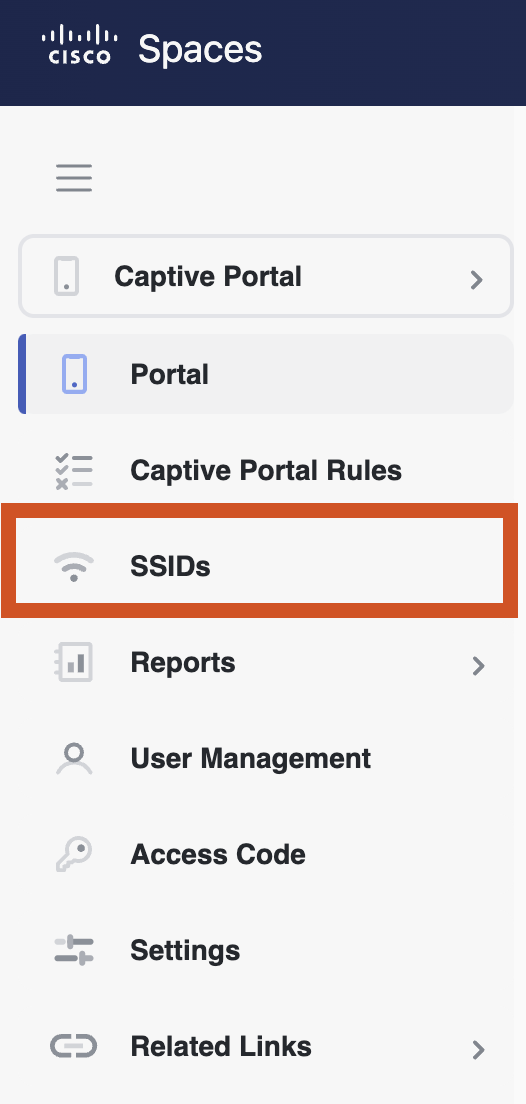
In Cisco Spaces, navigate to Captive Portal App -> Portal
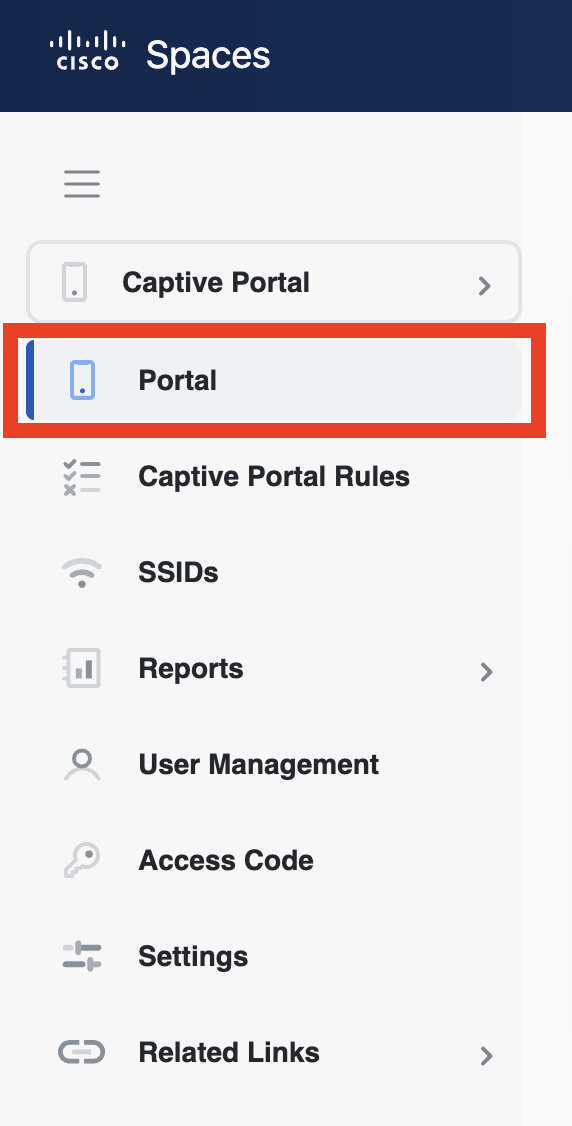
Either create a new portal or use one of the templates like Covid-19 specific templates. If using a templates, select a template and duplicate it for editing.
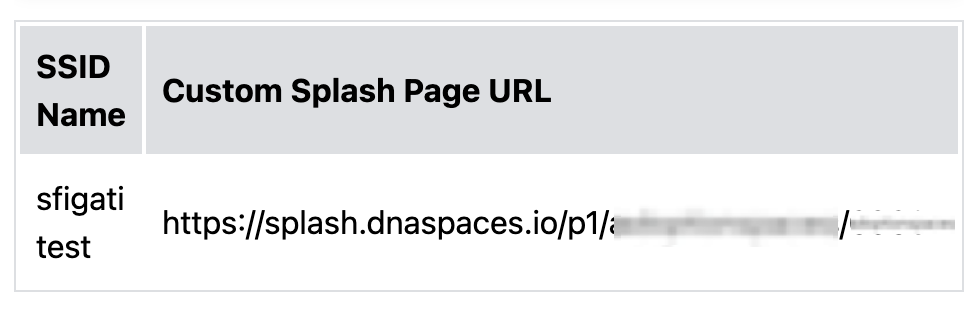
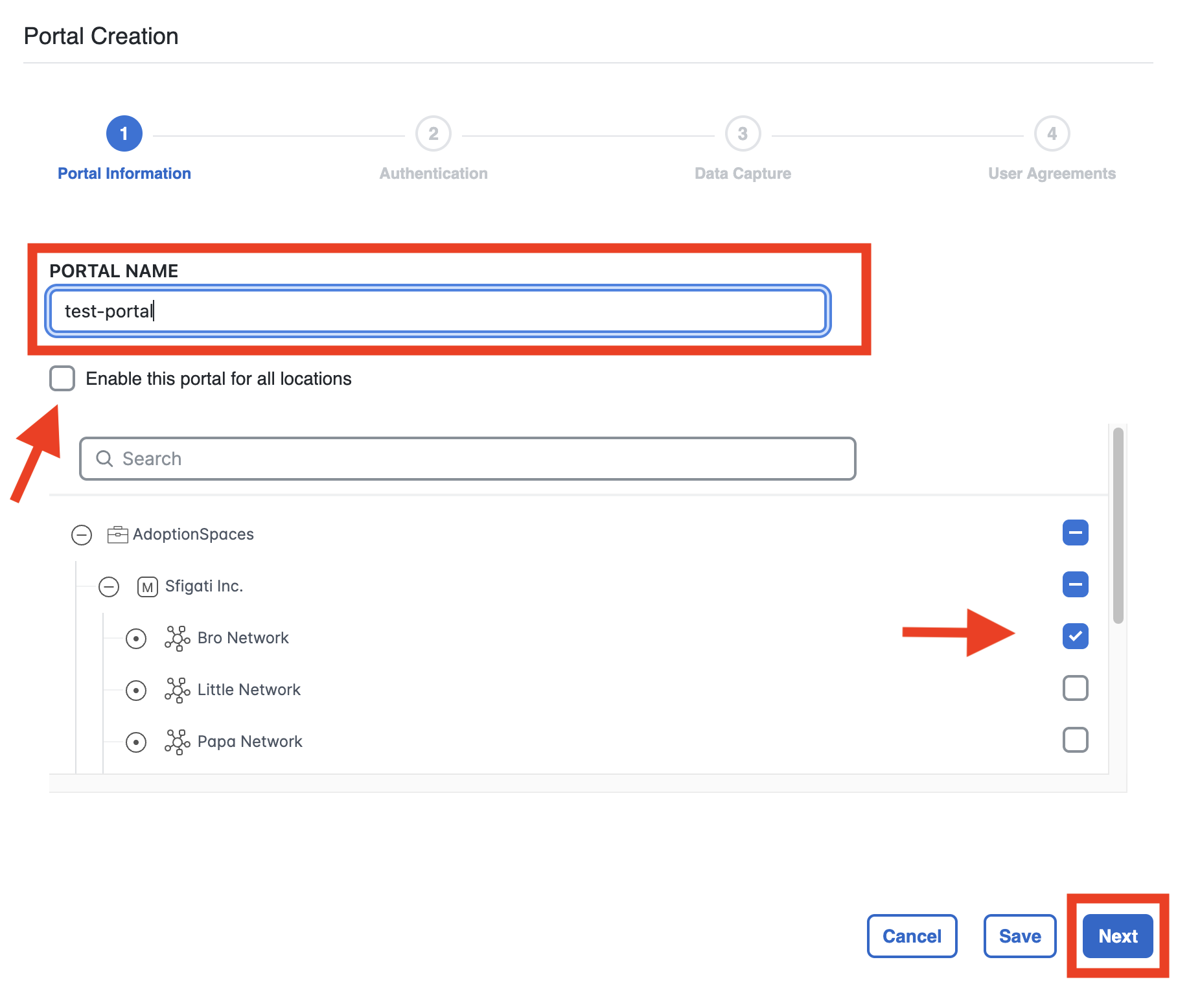
Enter a name for the portal and select the locations where this portal will be used. Select Next
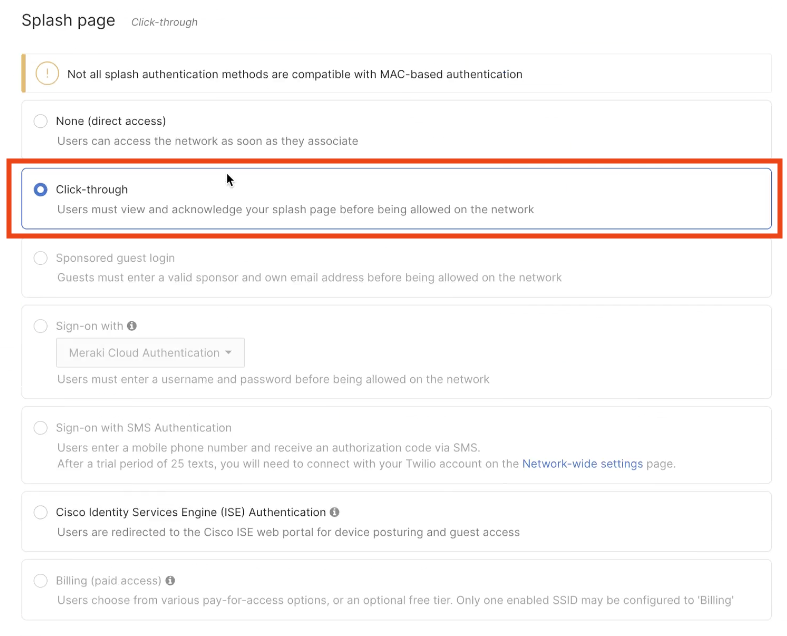
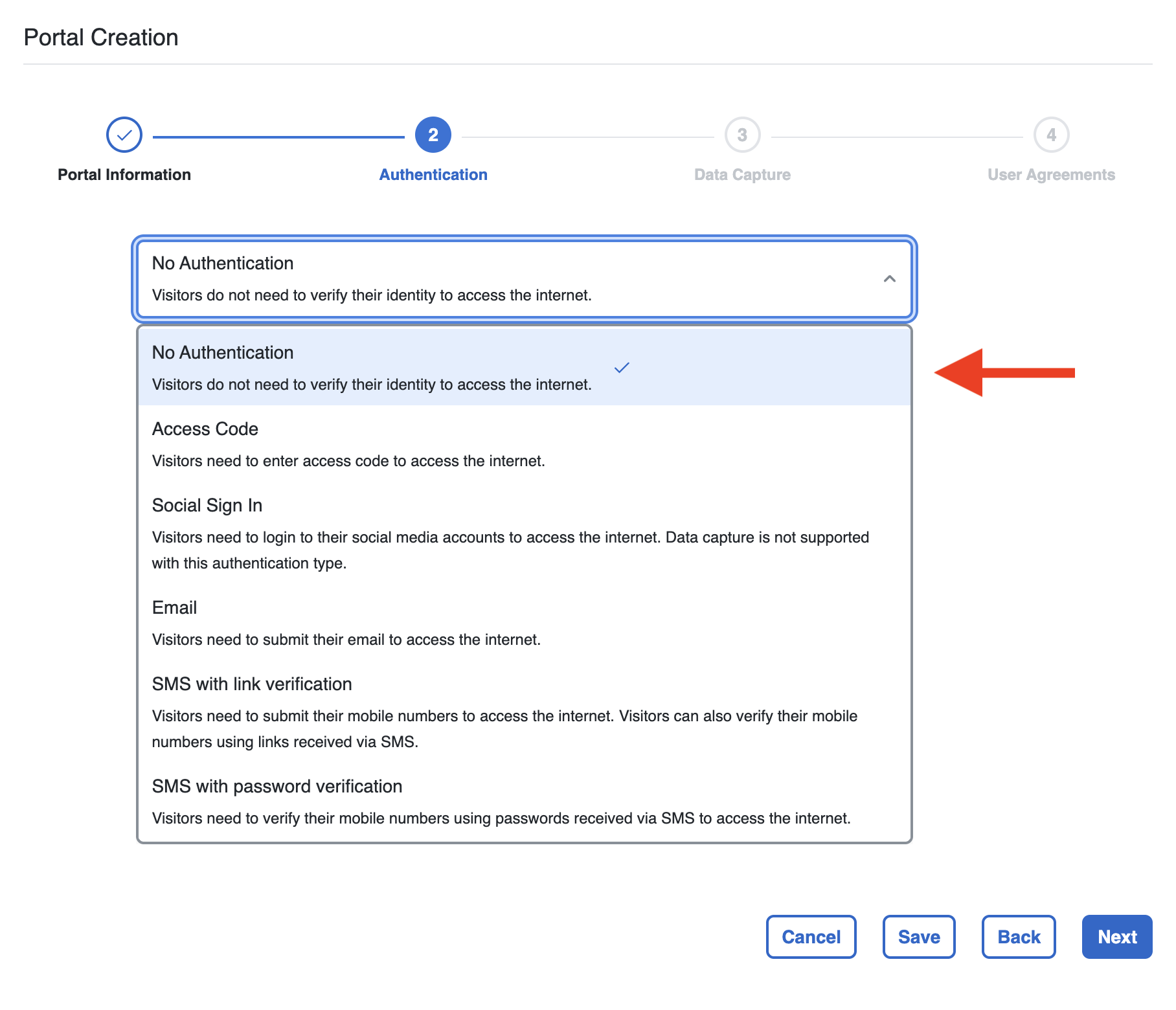
Select the authentication type as per need. For no specific authentications need, select No Authentication as an example.
For other Captive Portal Authentication methods, please refer to our Knowledge Article: [Coming Soon]
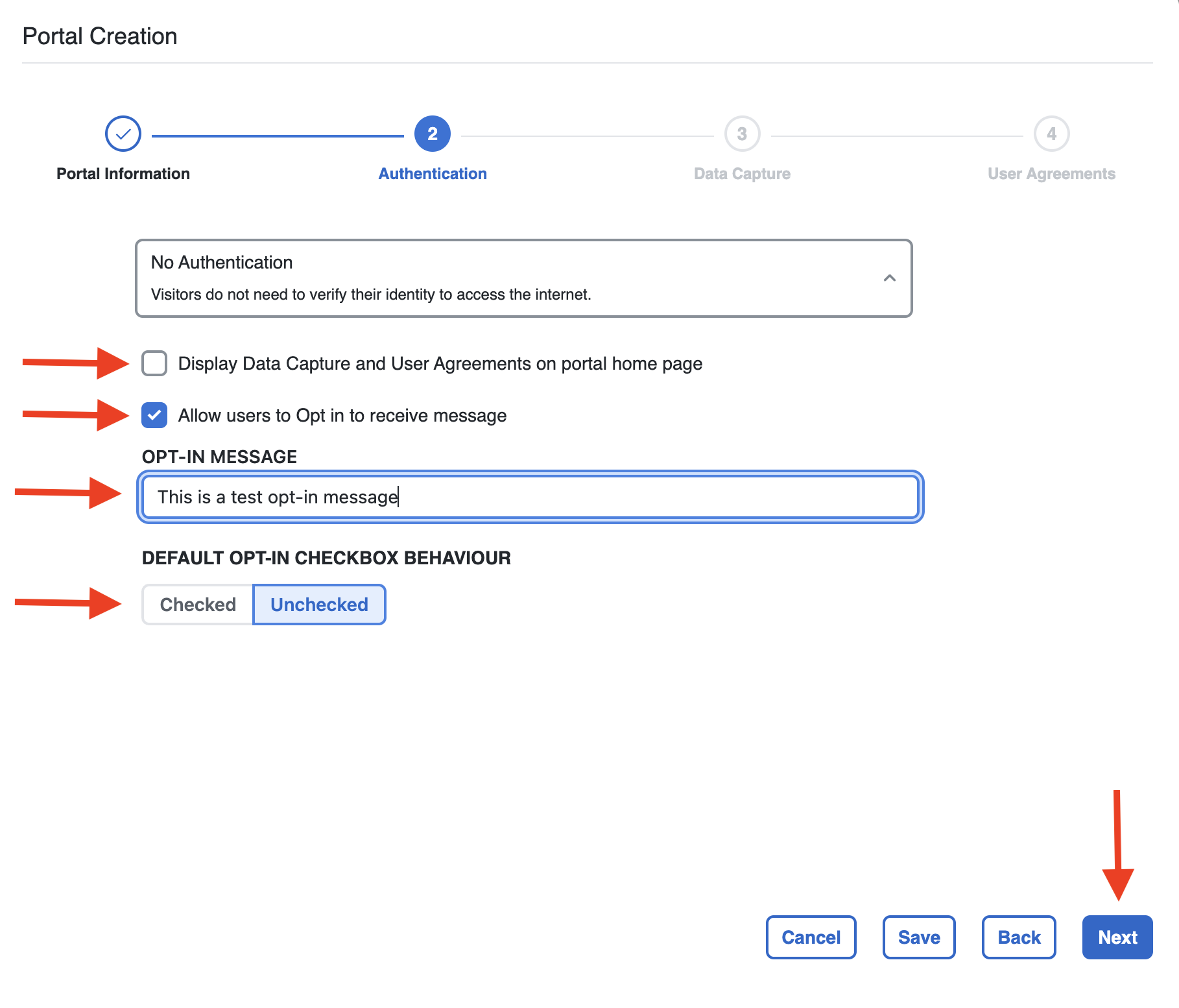
Choose if Data Capture and User Agreements need to be displayed on the portal. Remain unselected if not needed.
Choose if users need to specifically agree to opt-in the network. Put the opt-in message, choose the default behaviour.
If you want to show a specific Data Capture form that users must complete, enable Data Capture.
Multiple Fields are available to be chosen, and fields can be made mandatory to be completed by visitors.
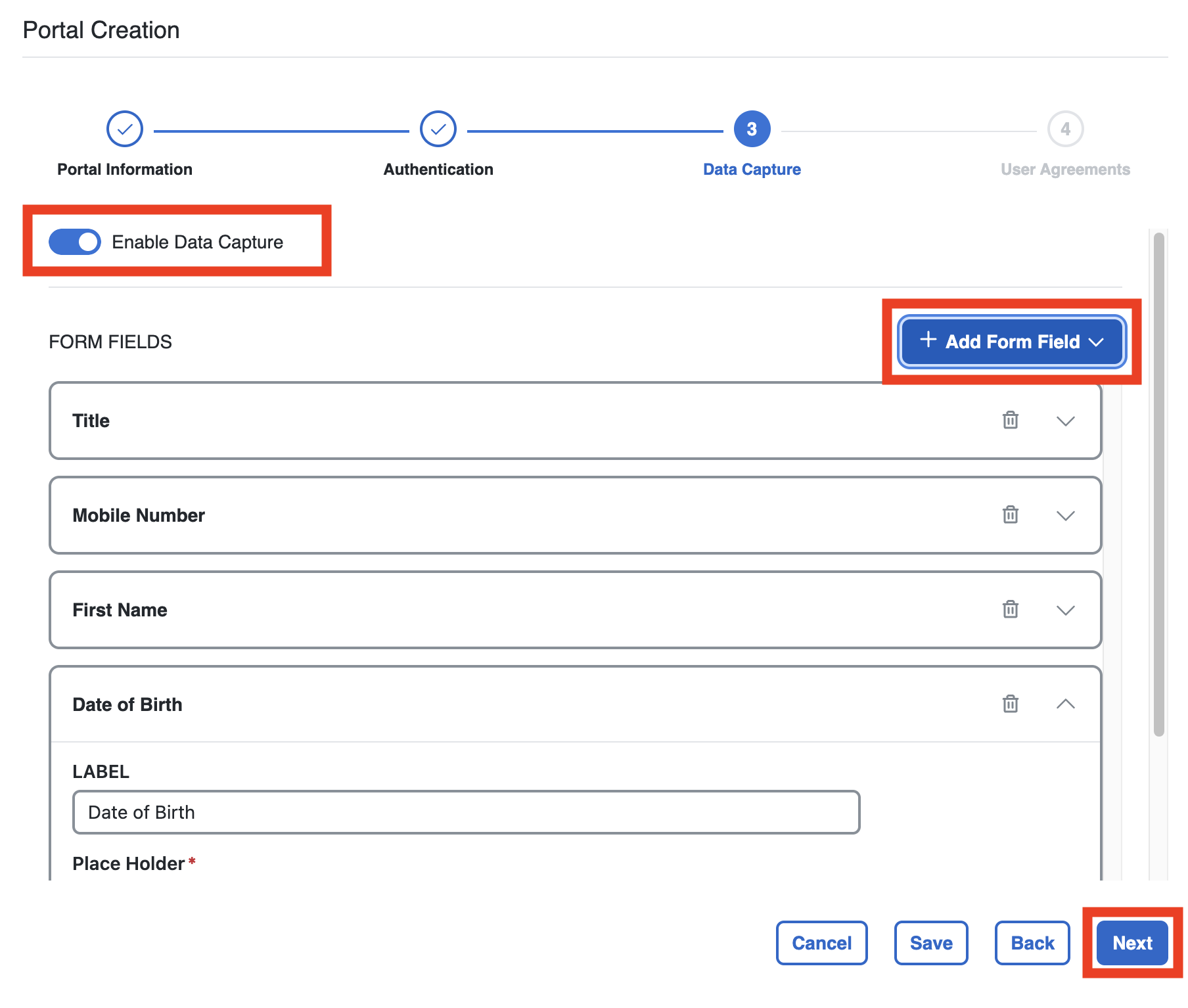
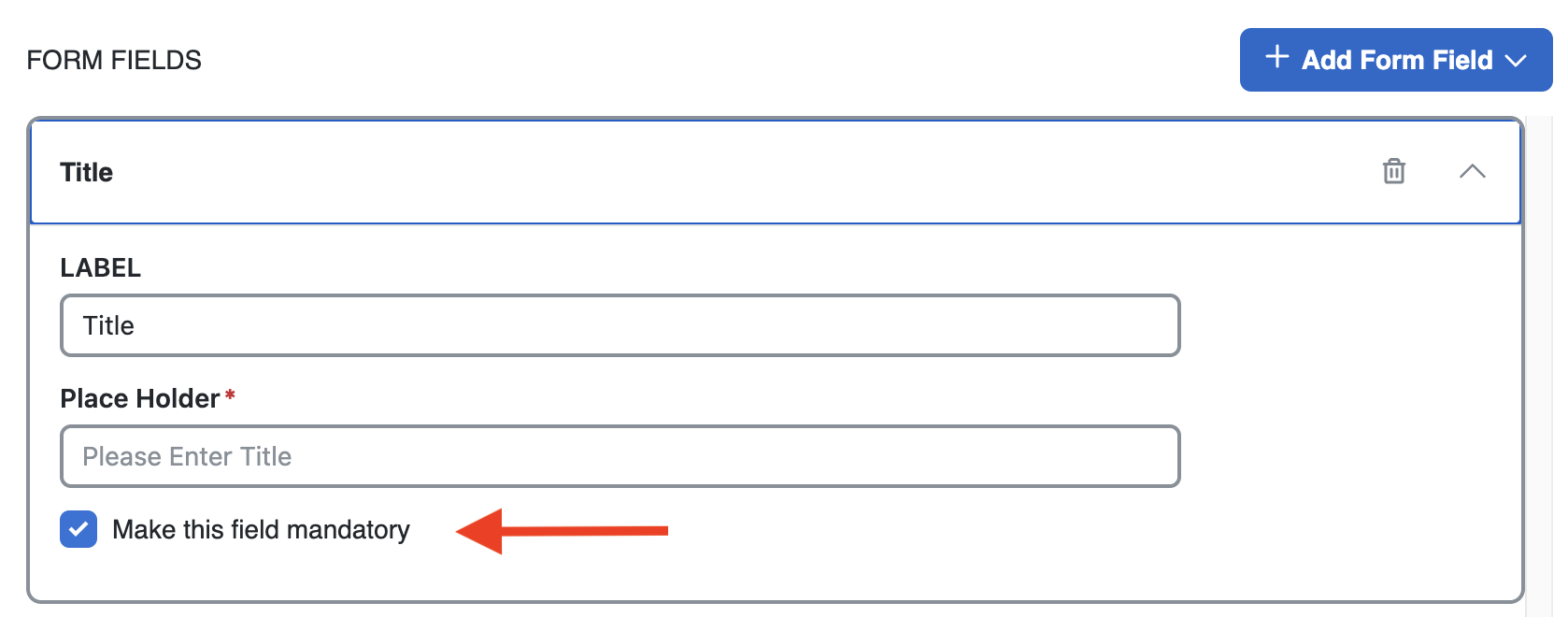
After all needed fields are chosen, click Next.
Select and configure the Terms and Conditions as necessary. Choose whether to Enable Terms and Conditions, Enable Privacy Policy or Age Gating.
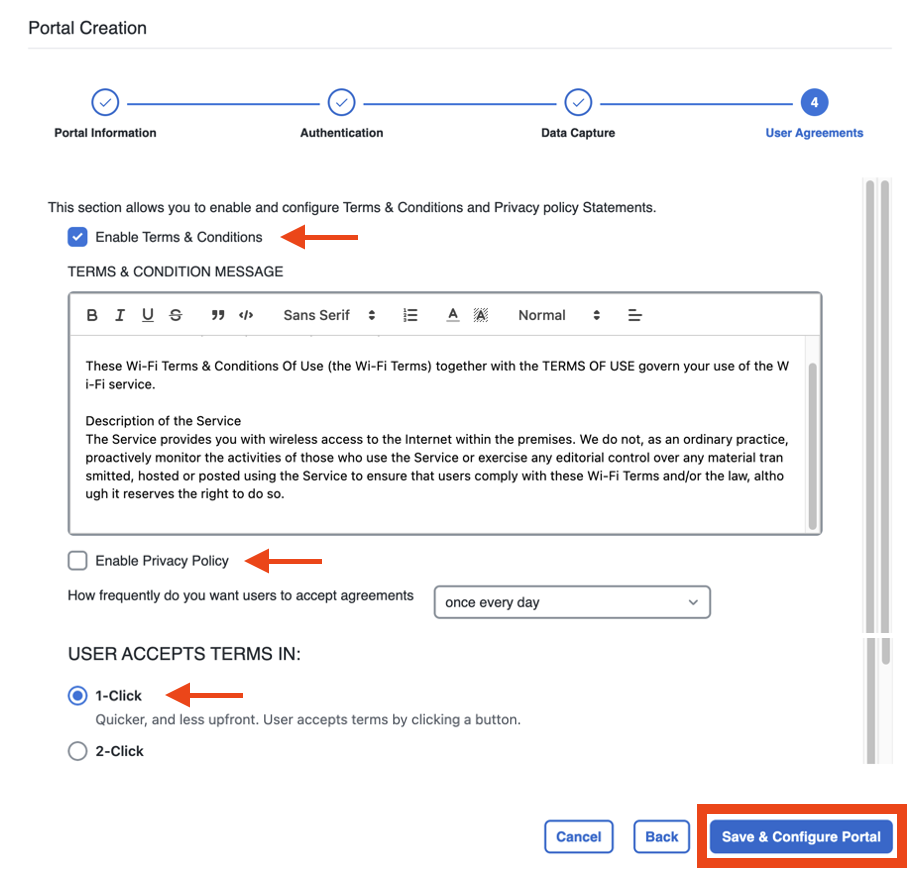
Select Save and Configure Portal when done.
Edit the Captive Portal Settings
Click the newly created portal to start editing it.
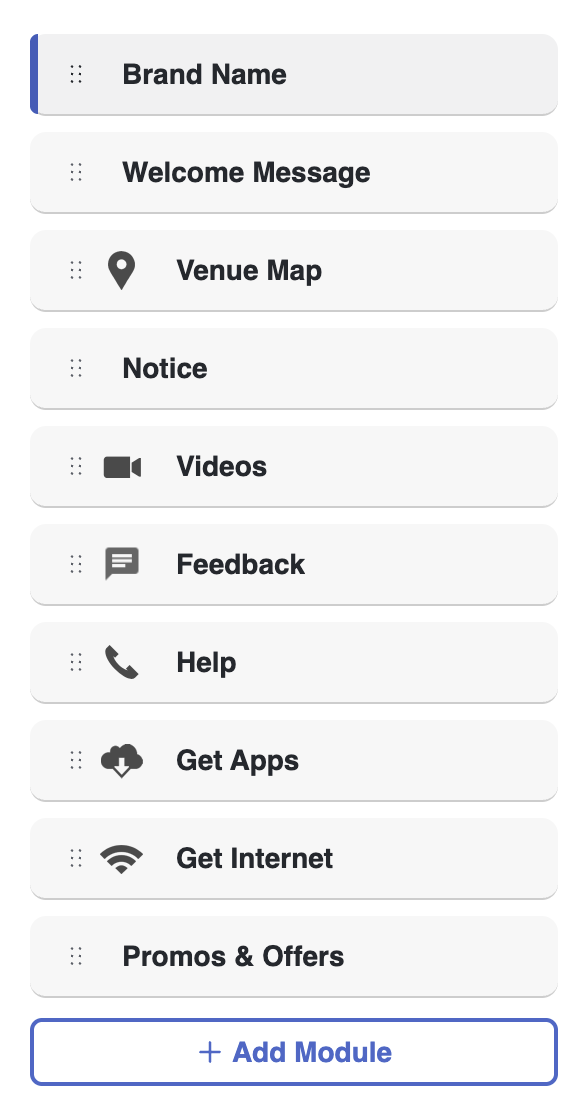
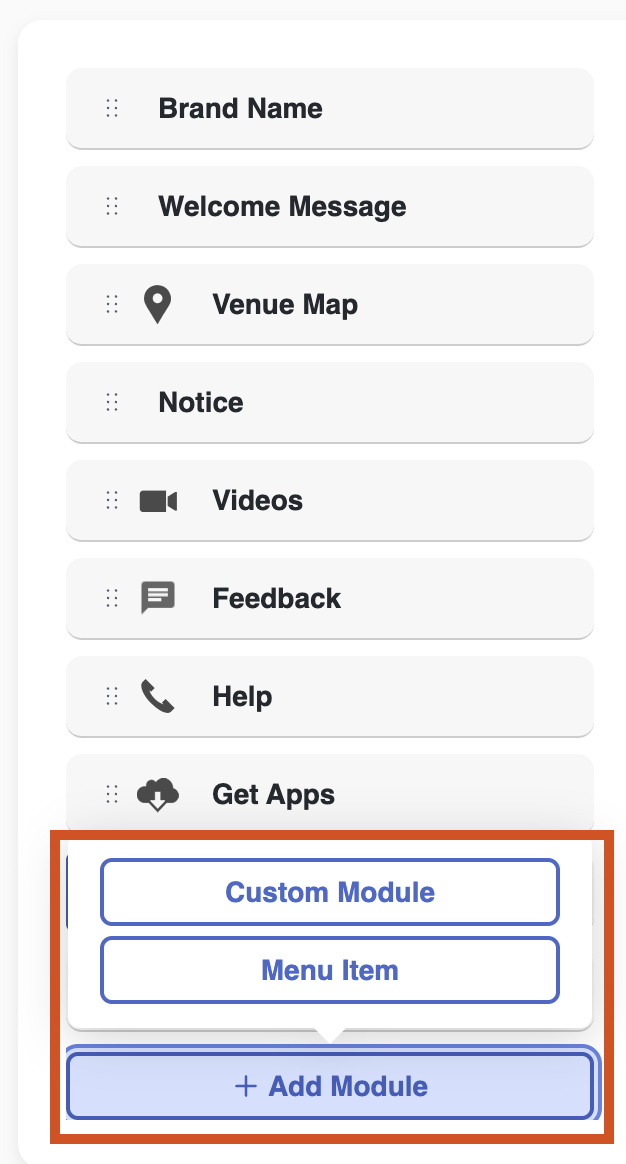
In the Portal Editor window, edit as well as reorder all the modules on the side panel by dragging and dropping them in the desired sequence.
Type in any required welcome message. You can preview the look and feel of the Captive Portal page on the right-side Portal Preview panel that renders draft-changes live.
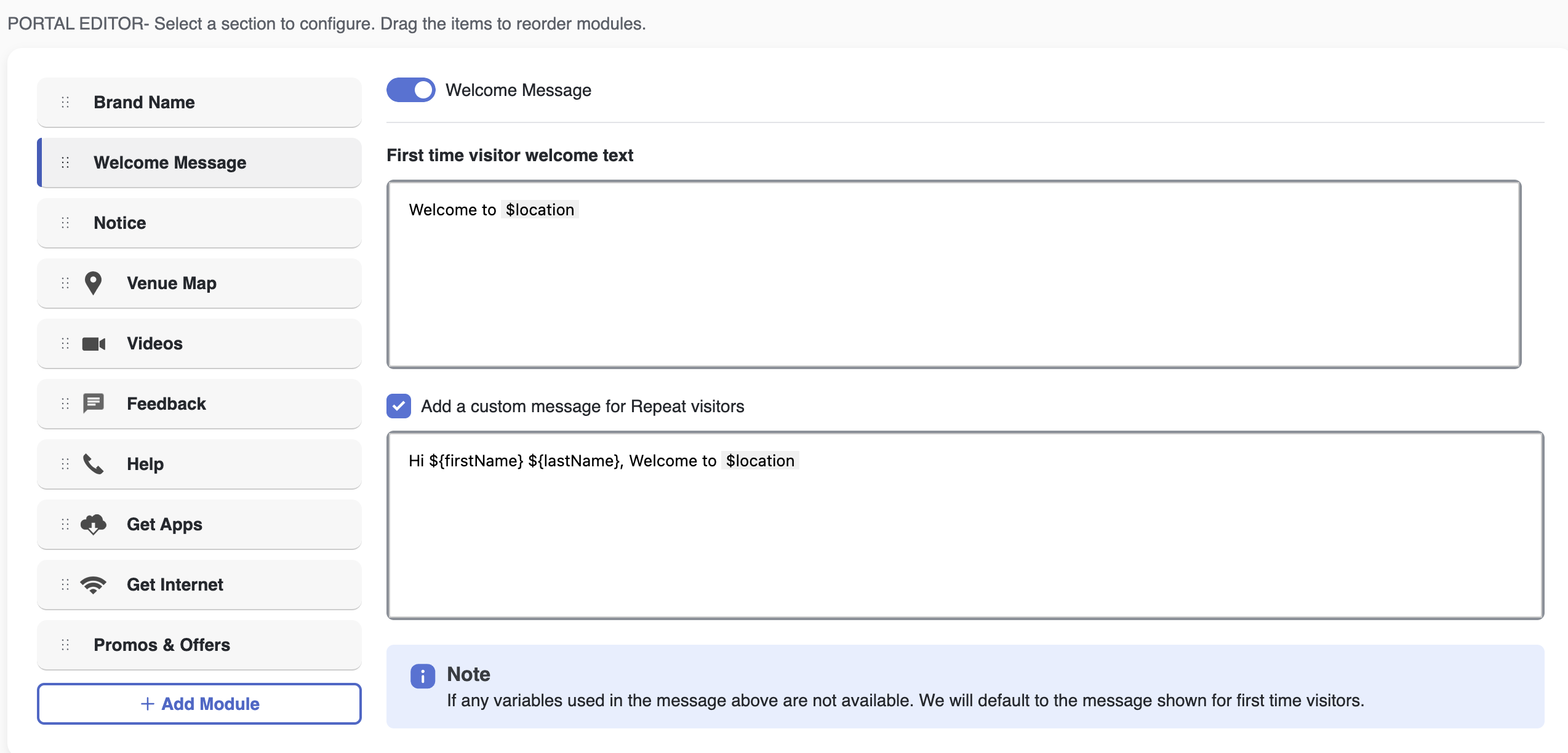
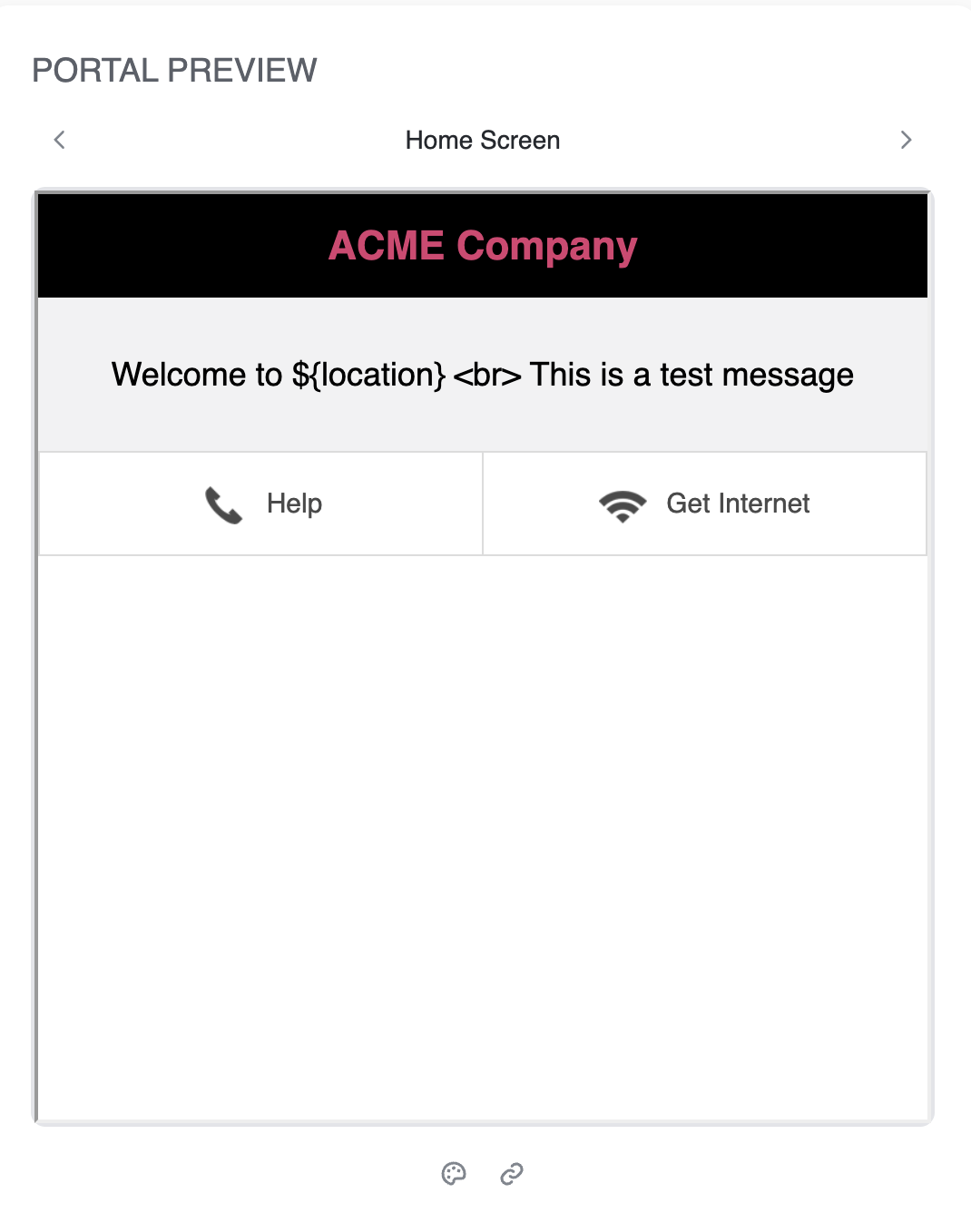
Smart variables can also be added in the messages using $<key>.
Smart Variable | Description |
|---|---|
$location | Location Name as per Hierarchy |
$Address | Address of the location |
$State | State of the location |
$Zipcode | Zip Code of the location |
$Country | County of the location |
$City | City of the location |
These variables in this Portal Editor section pertains to the properties of the location where the client is connecting - i.e. which buildings, floor etc.
The Landing page upon success can be edited by clicking Get Internet
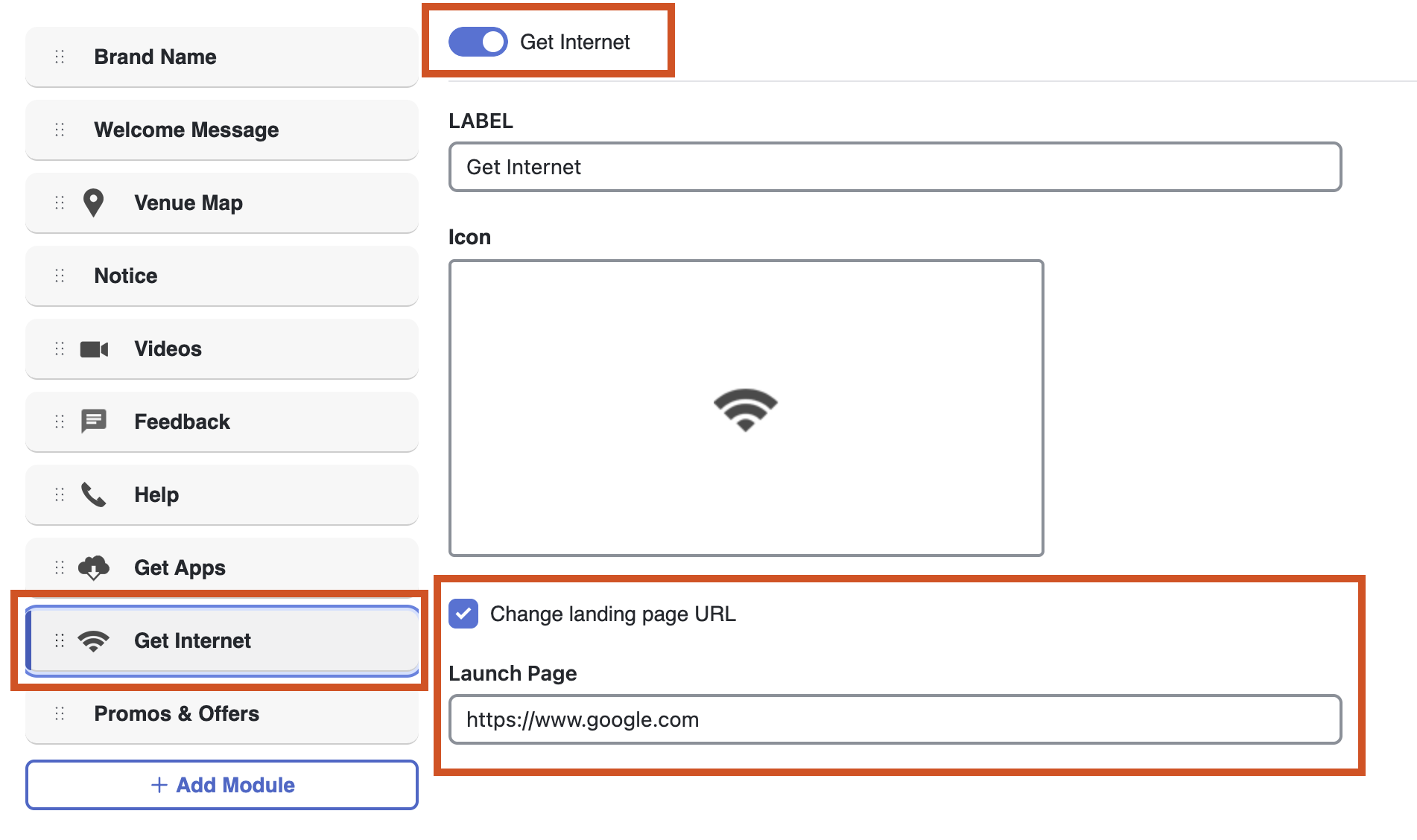
New modules can be added directly with additional content.
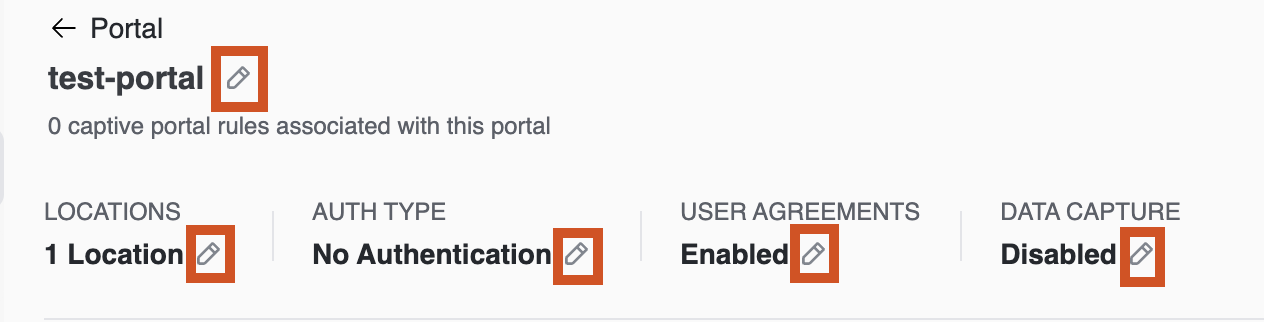
Any previous configurations can be edited by clicking the pencil icon on top of the Portal Editor page.
Create Portal Rules
Navigate to Cisco Spaces and then, Captive Portal App -> Captive Portal Rules
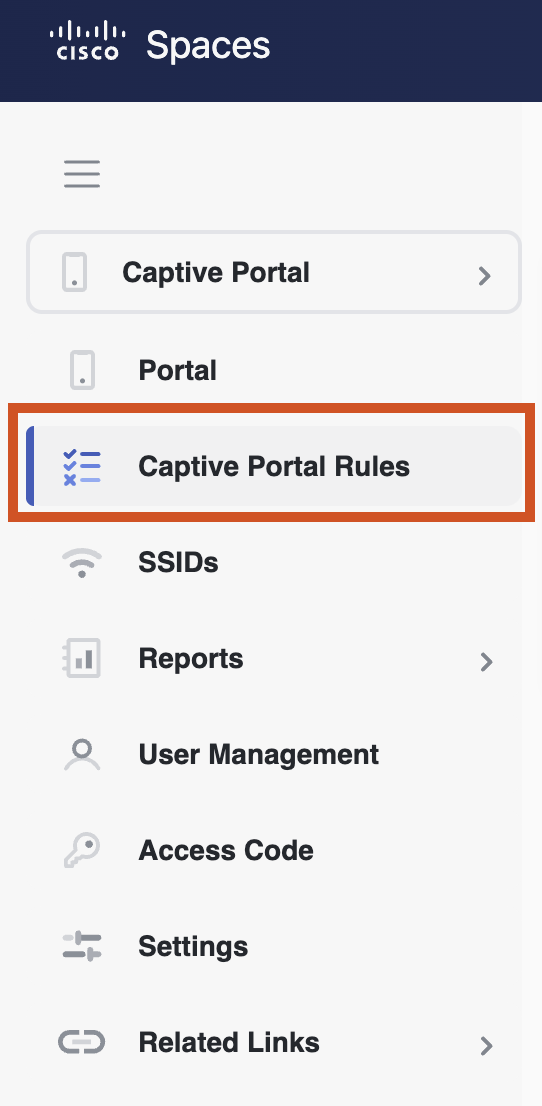
Create a new rule to make a specific rule to be triggered as needed by click Create New Rule.
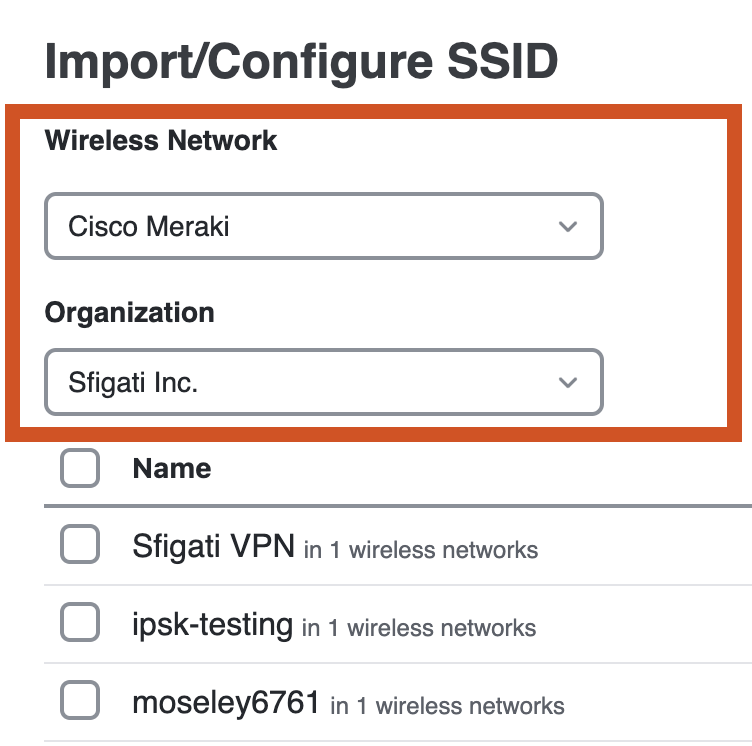
Enter a name for the rule. Select which SSID is this rule going to triggered against. The SSID should have already been imported / configured from earlier steps.
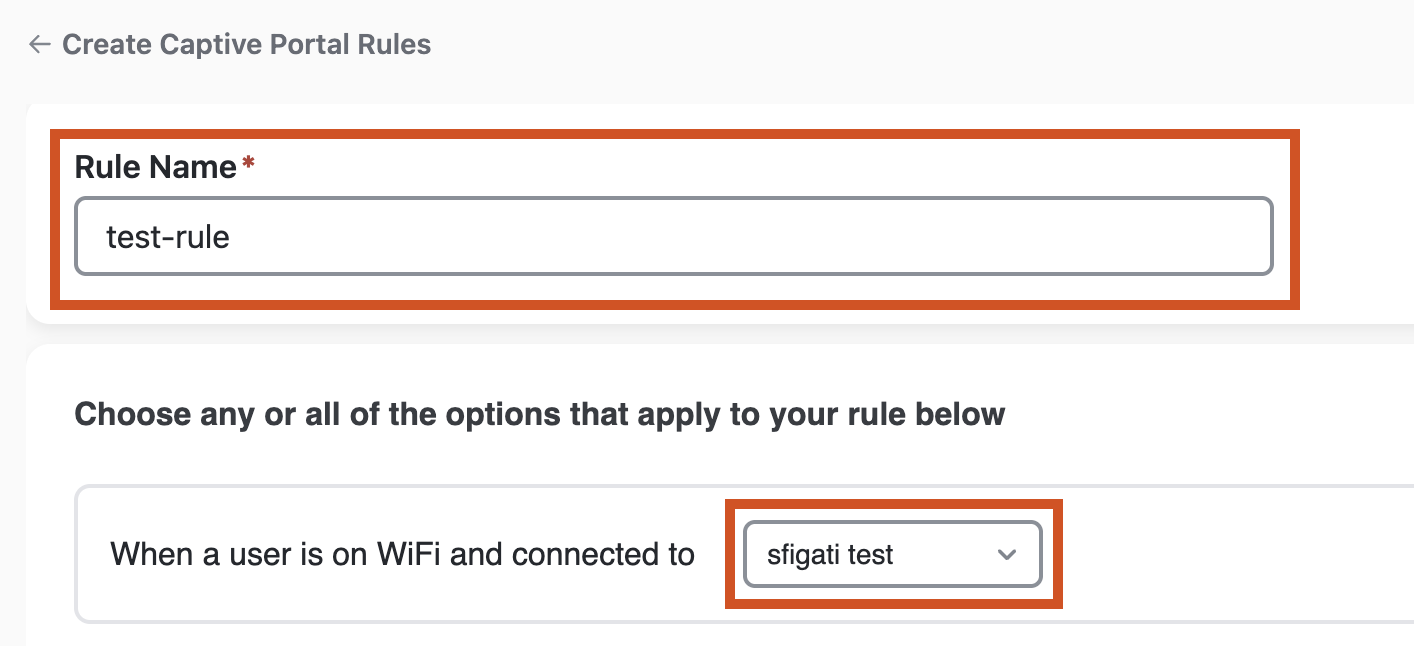
Add a location against which this rule should be be triggered. At least one location level needs to be selected.
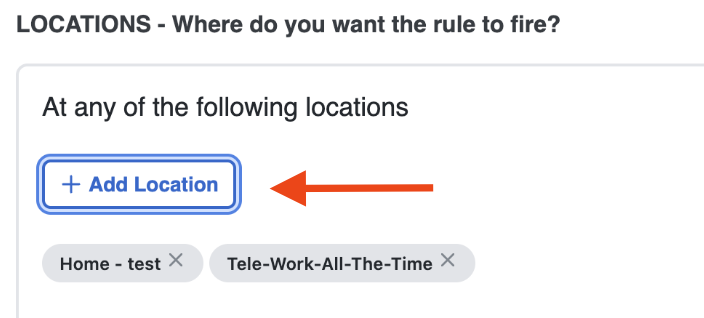
Location needs to be chosen from existing location hierarchy and can be chosen all the way from entire campus levels all the way down to a single zone on a floor.
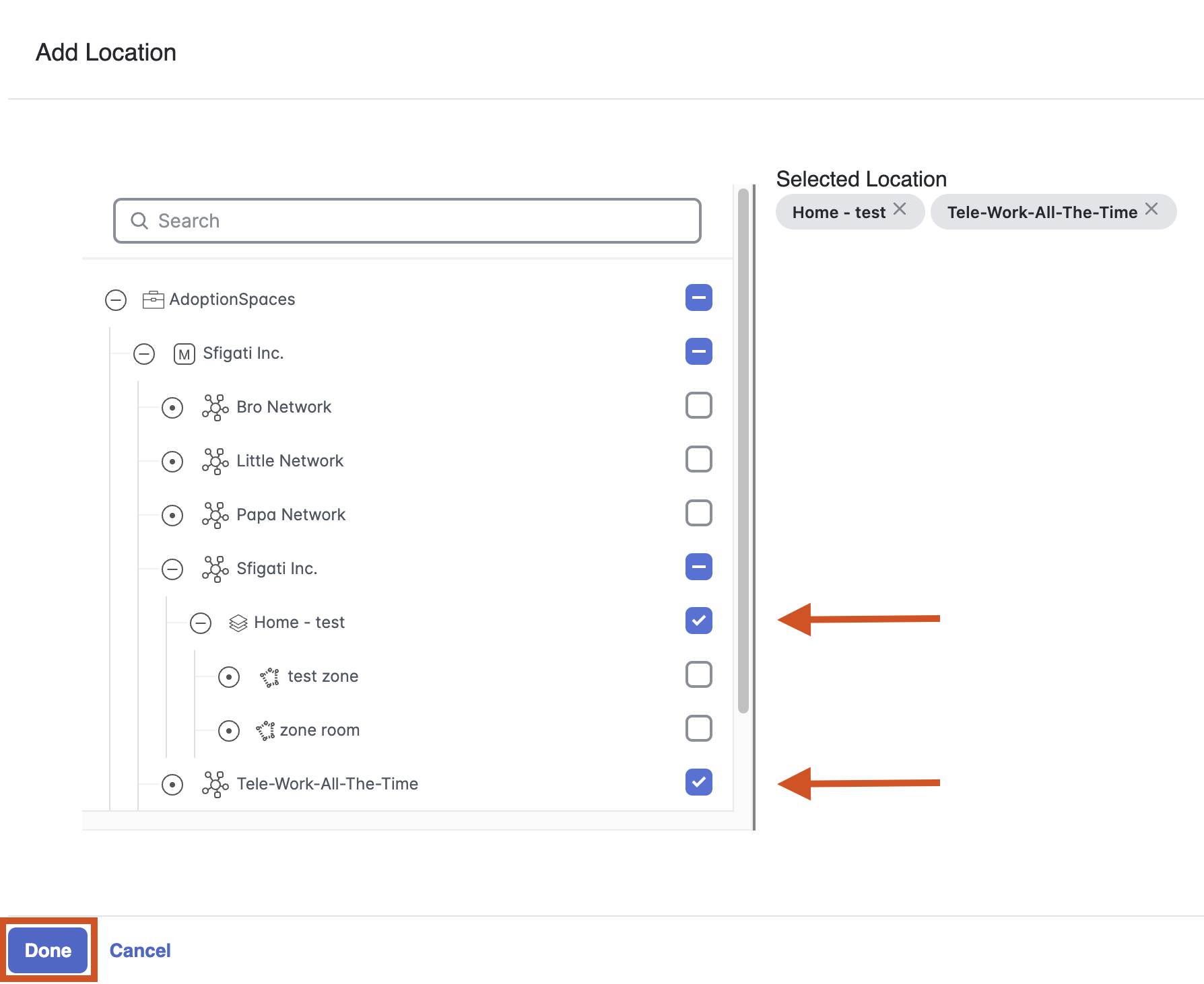
Any mix of locations can be selected inc. AireOS, Catalyst or Meraki networks. Click Done once the networks are selected.
The rule will be triggered only if a client is connecting on an AP that exists in the selected location.
In the Locations Section, if the location hierarchy has metadata tags in use, the rule can also be triggered against very specific locations. Example Use Case: Exclude “yet to open” sites and include “recently opened” sites for a new portal campaign.
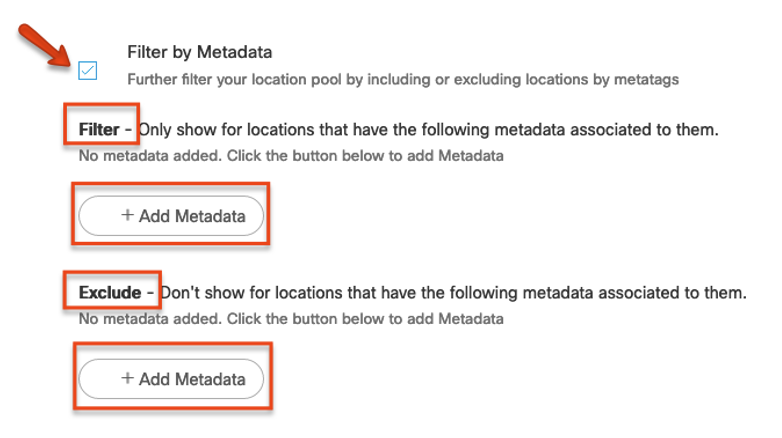
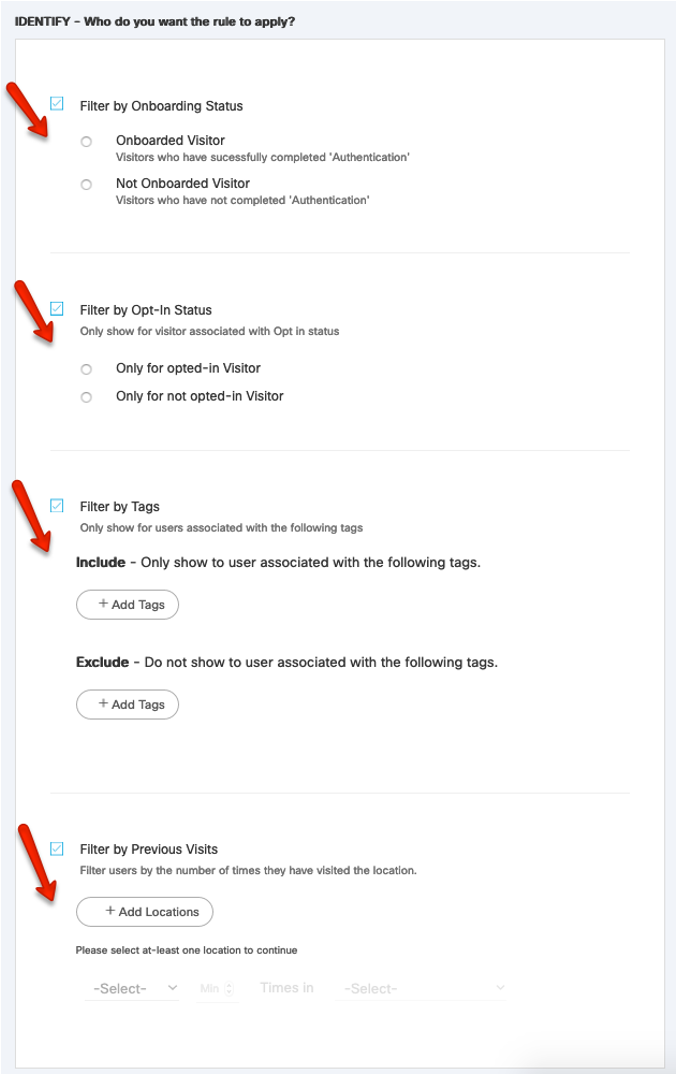
In the Identify section, multiple selections are available to be tweaked. Cisco Spaces saves mac-address used by clients to achieve these filters. The table below details the options:
Identify Filter | Function |
|---|---|
Filter by Onboarding Status | Allows to chose a particular action or portal for visitors who have already completed captive portal authentications previously or not. |
Filter by Opt-In Status | Allows to chose a particular action or portal for visitors who have specifically chosen to opt-in. |
Filter by Tags | Captive Portals application and Location Personas application can tag visitors with specific tags based on their on-location behavior. This tags can be used to trigger a specific action or portal for specific visitors. |
Filter by Previous Visits | Allows to chose a particular action or portal based on whether a client has come into a specific location at least a specific number or between a number of times in particular days or day ranges |
In the Actions Section – multiple selections are available. The table below details the options:
Actions | Function |
|---|---|
Show Captive Portal | A specific portal that is created can be chosen to be shown. Different rules can be created to show different types of portals |
Seamlessly Provision Internet | This option can be used to avoid showing the portal and directly onboard visitors’ devices. |
Deny Internet | This option can be used to reject the device association. |
Furthermore, a tag can be created to be assigned to visitors that match all the rules and get successfully onboarded to the network.
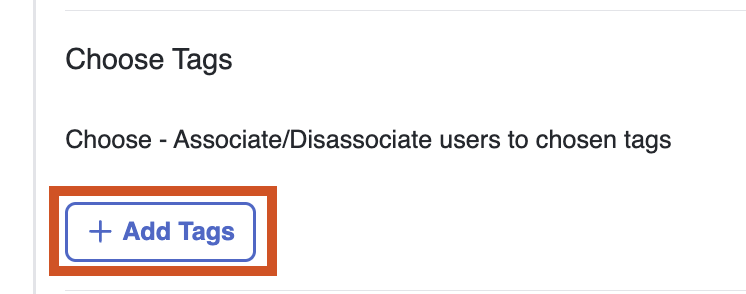
External APIs can be triggered when a new client is onboarded for the very first time. For triggering an API every time a client is successfully onboarded, ‘Enable for repeat visitors’ can be selected.
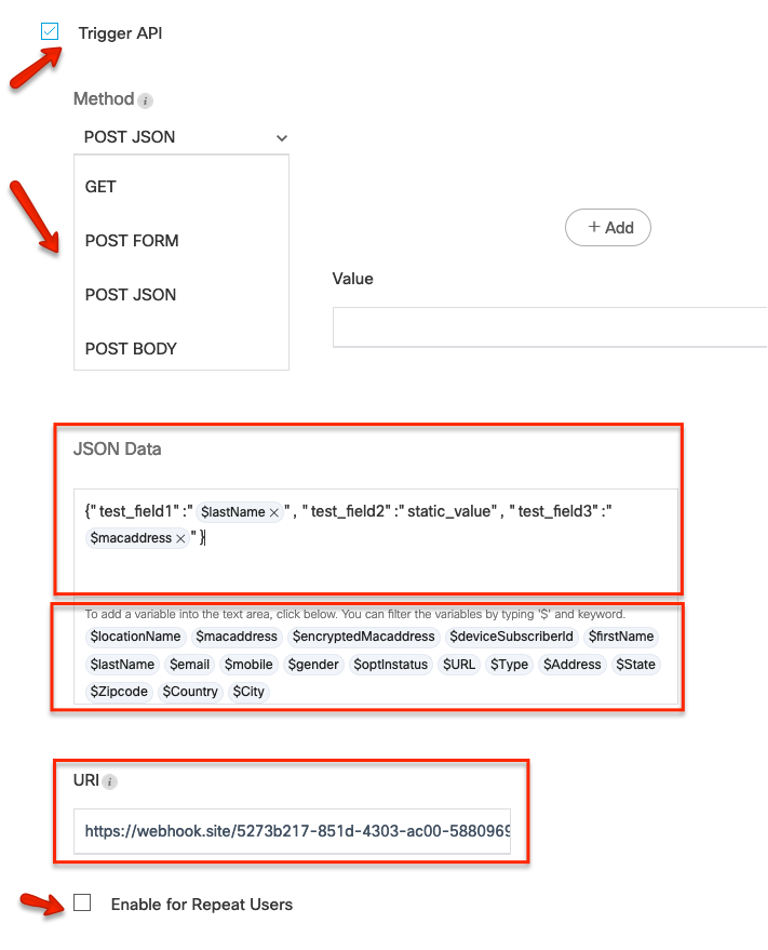
These variables in this API section pertains to the properties of the visitor that is connecting. (Example: visitor name, gender etc.)
Many variables like email, name, address etc. are only available if they were captured for the same visitor using the Data Capture form in the portal.
The following Smart Variables are available in Captive Portals API:
Variable Details | Smart Variables |
|---|---|
Location Name | $locationName |
Address | $Address |
Mac-address | $macaddress |
Mobile | $mobile |
State | $State |
Encrypted Mac-address | $encryptedMacaddress |
Gender | $gender |
Zip Code | $Zipcode |
Device subscriber ID | $deviceSubscruberId |
Opt in Status | $optinstatus |
Country | $Country |
First Name | $firstName |
URL | $URL |
City | $City |
Last Name | $lastName |
Type | $Type |
View the overall created rule in the summary section on the right-side of the dashboard.
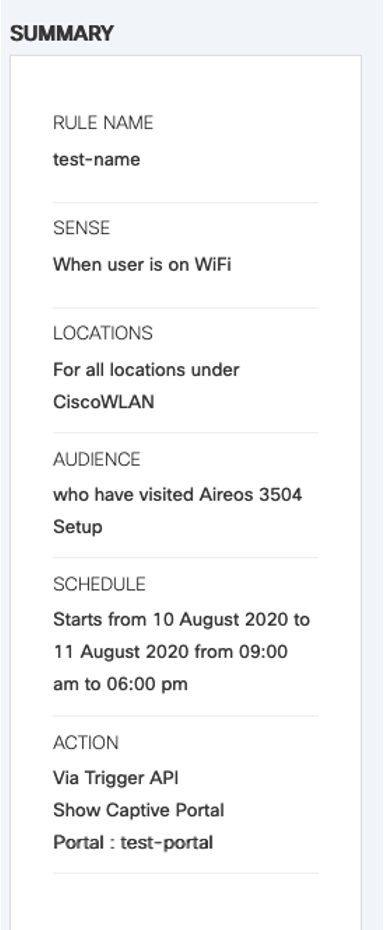
If satisfied with the rule, click Save & Publish.
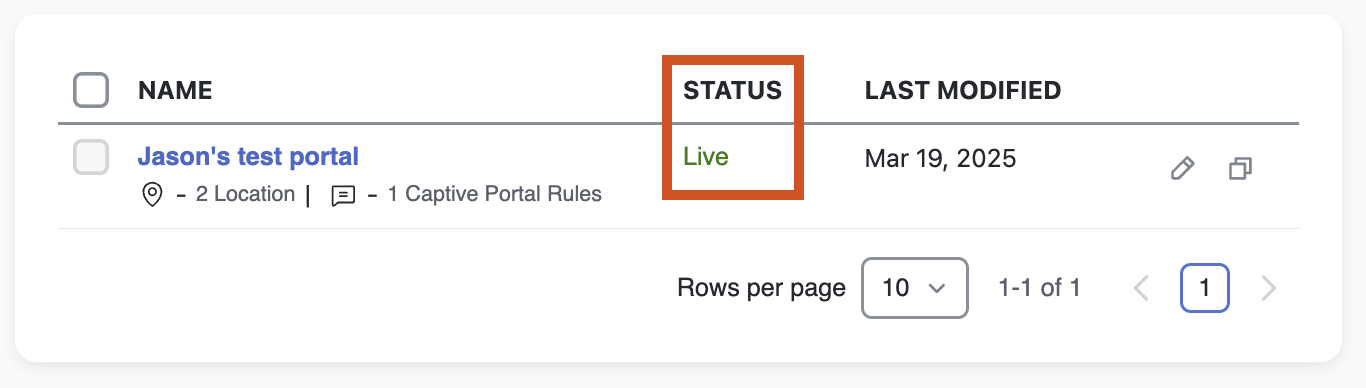
Once the rule is pushed, the Captive Portal will show up as being Live in the Portal window.
FAQ
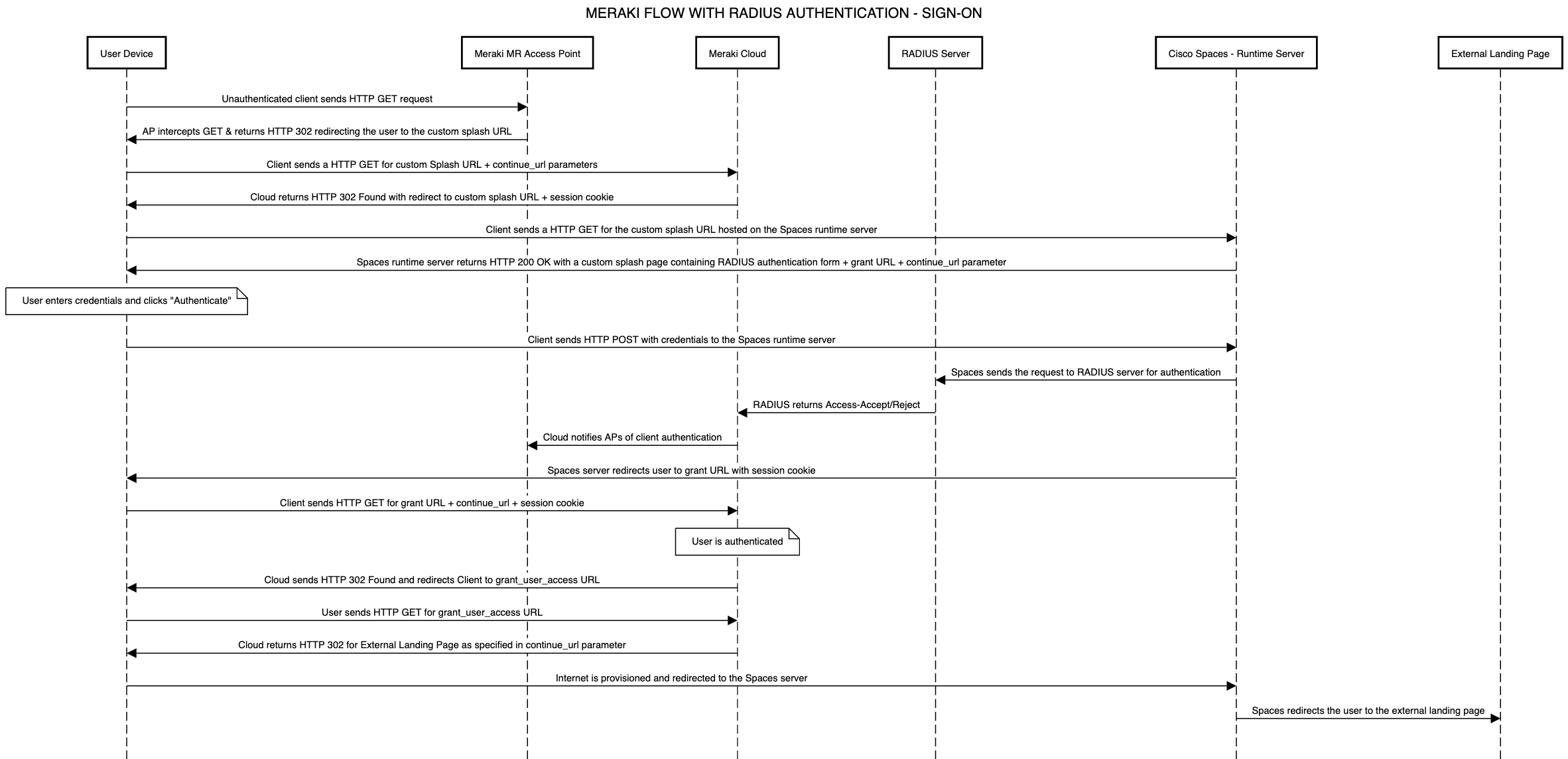
What does the complete data flow look like from guest end-device to having Captive Portal provision Internet?
Meraki Data Flow (with Radius)
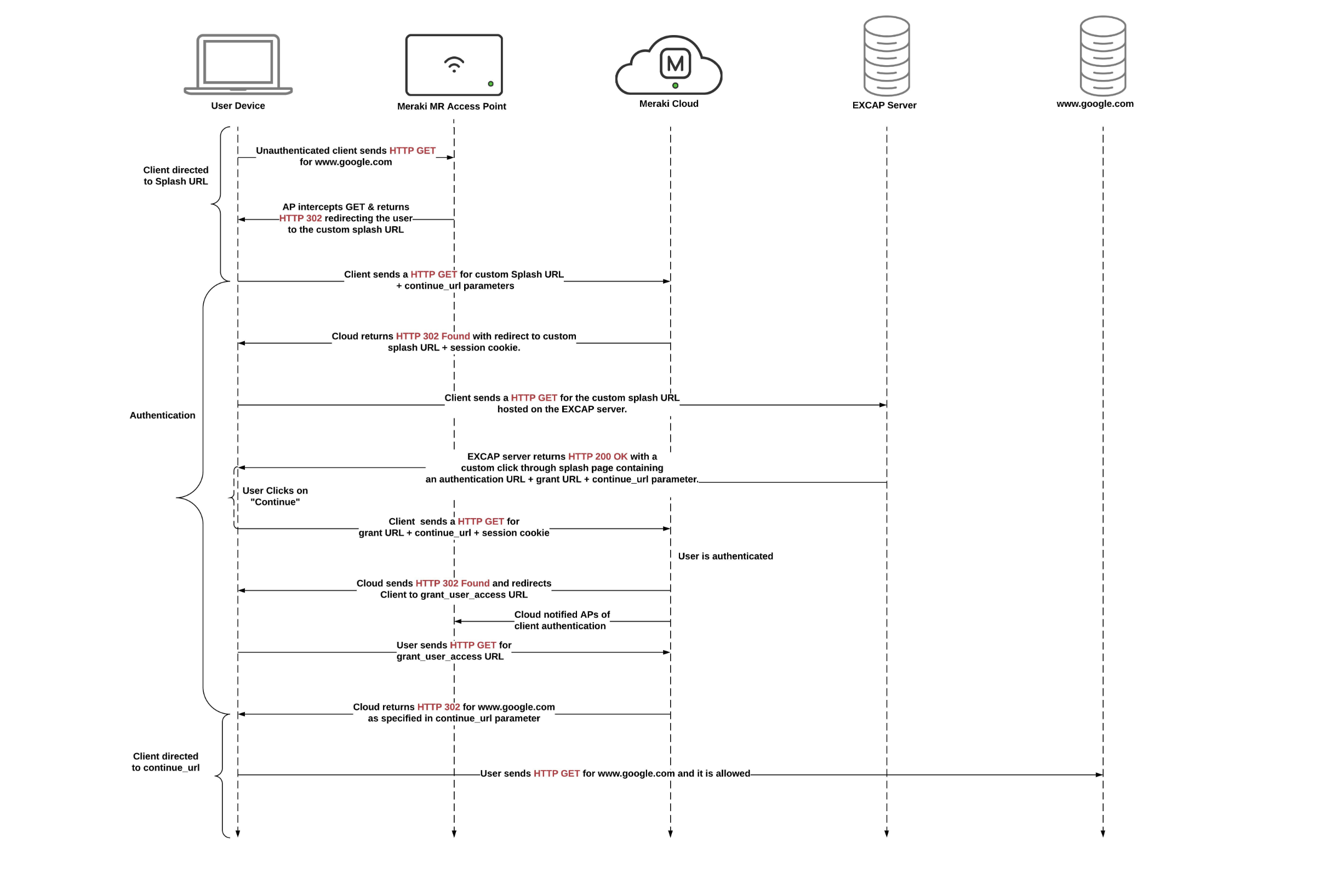
Meraki Data Flow (without Radius)
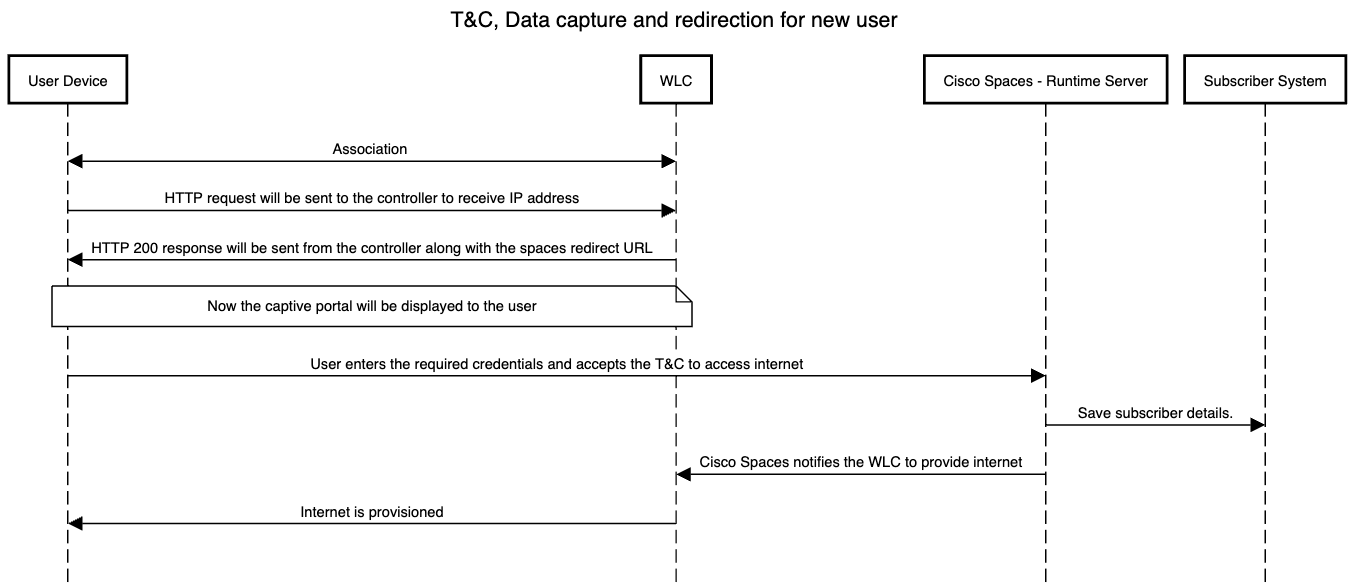
Catalyst Data Flow (with Radius)
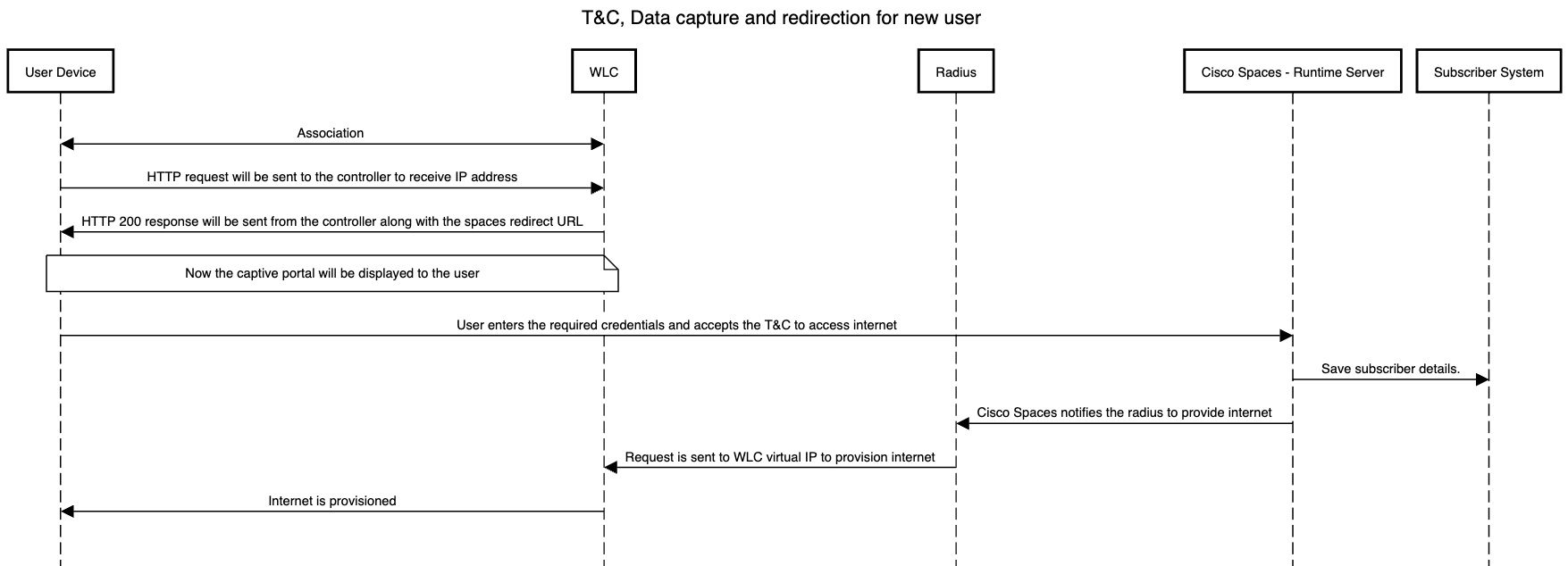
Catalyst Data Flow (without Radius)
What if my certificate authority won’t issue a certificate for the Catalyst 9800’s virtual IP (192.0.2.1)?
When configuring a Captive Portal on a Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controller, it’s essential to install a trusted SSL/TLS certificate that matches the controller’s virtual interface IP address or DNS name. Without a trusted certificate, users will encounter browser security warnings when redirected to the captive portal.
The virtual IP address used by the Catalyst 9800 is typically 192.0.2.1, which is a reserved, non-routable address used internally by the controller.
However, many public Certificate Authorities (CAs) will not issue certificates that include private or reserved IP addresses (such as 192.0.2.1) in the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) field, as this violates industry standards and CA policies.
Workaround:
To resolve this, use a domain name instead of the IP address in the certificate’s SAN field.
Example 1:
WLC virtual IP:
192.0.2.1Chosen domain:
wlc-portal.company.comInternal DNS record:
wlc-portal.company.com → 192.0.2.1Certificate SAN:
DNS:wlc-portal.company.com(no IP addresses)
Example 2:
WLC virtual IP:
192.0.2.1Chosen domain:
guestwifi.melbournebranch.localInternal DNS record:
guestwifi.melbournebranch.local → 192.0.2.1Certificate SAN:
guestwifi.melbournebranch.local(no IP addresses)
Follow these steps:
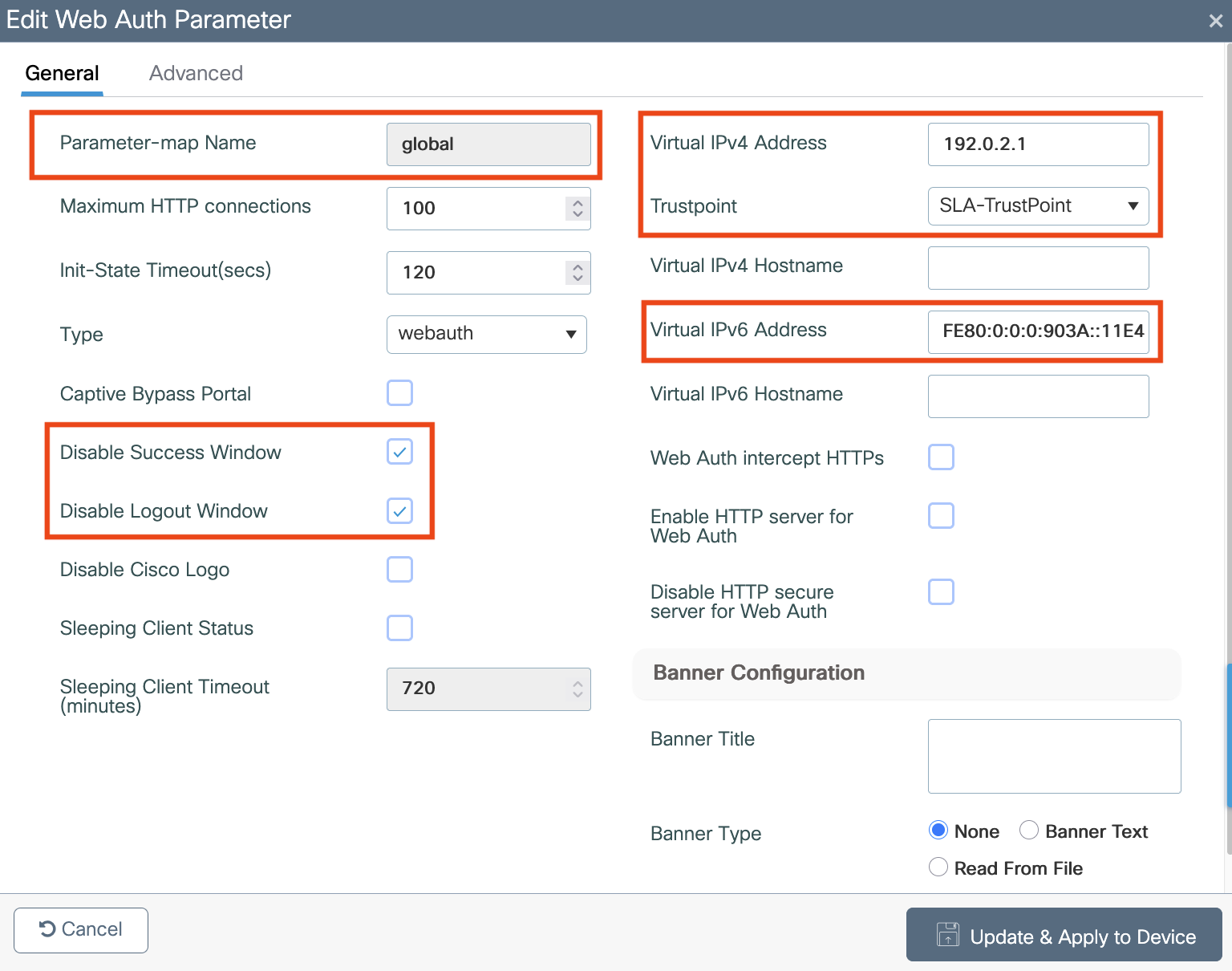
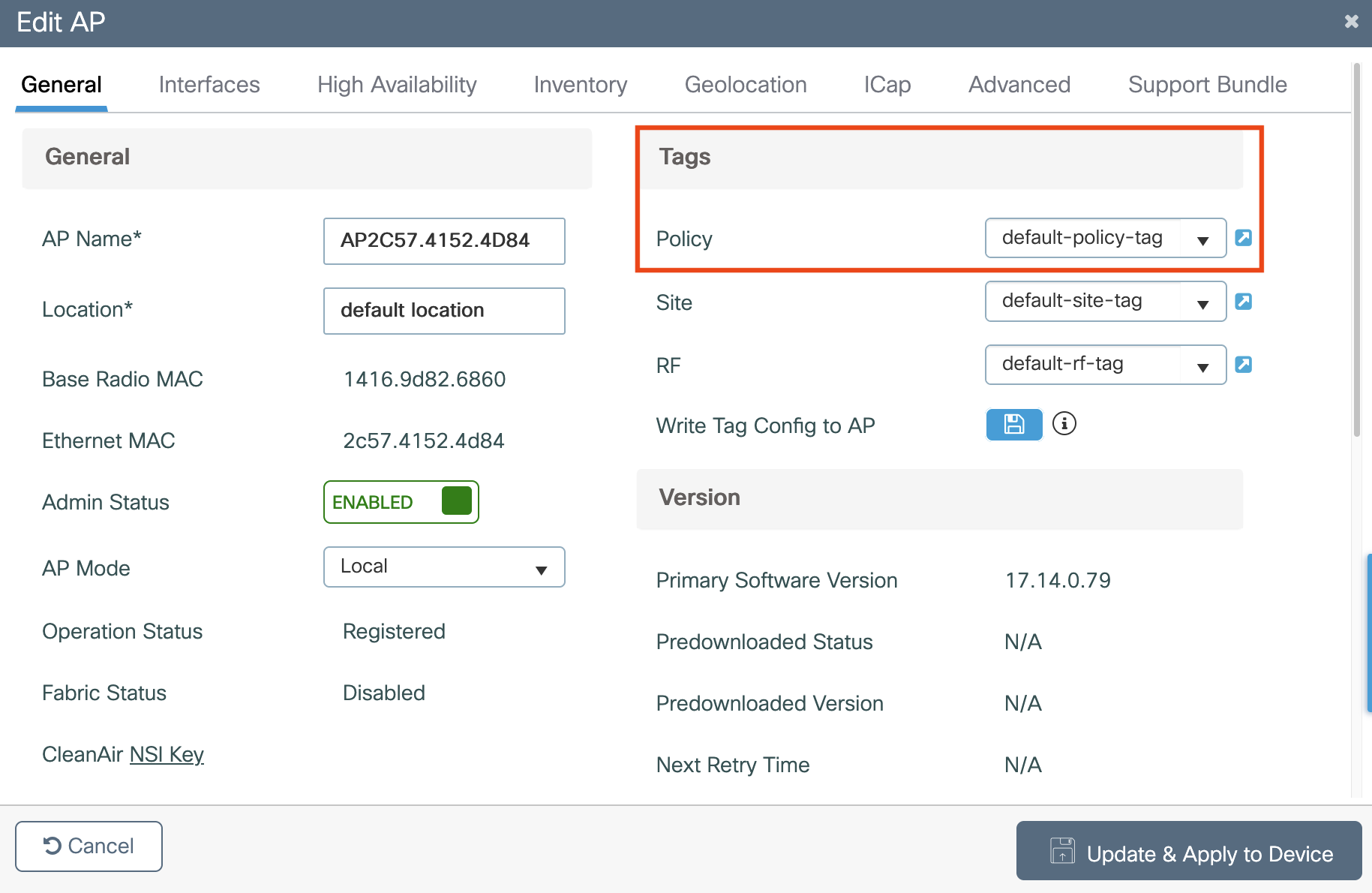
Choose a Domain Name: Select a unique domain name (e.g.,
wlc-portal.example.com) to represent the WLC’s virtual interface.Configure the WLC: In the Catalyst 9800 configuration, set the virtual interface’s DNS name to the chosen domain name.
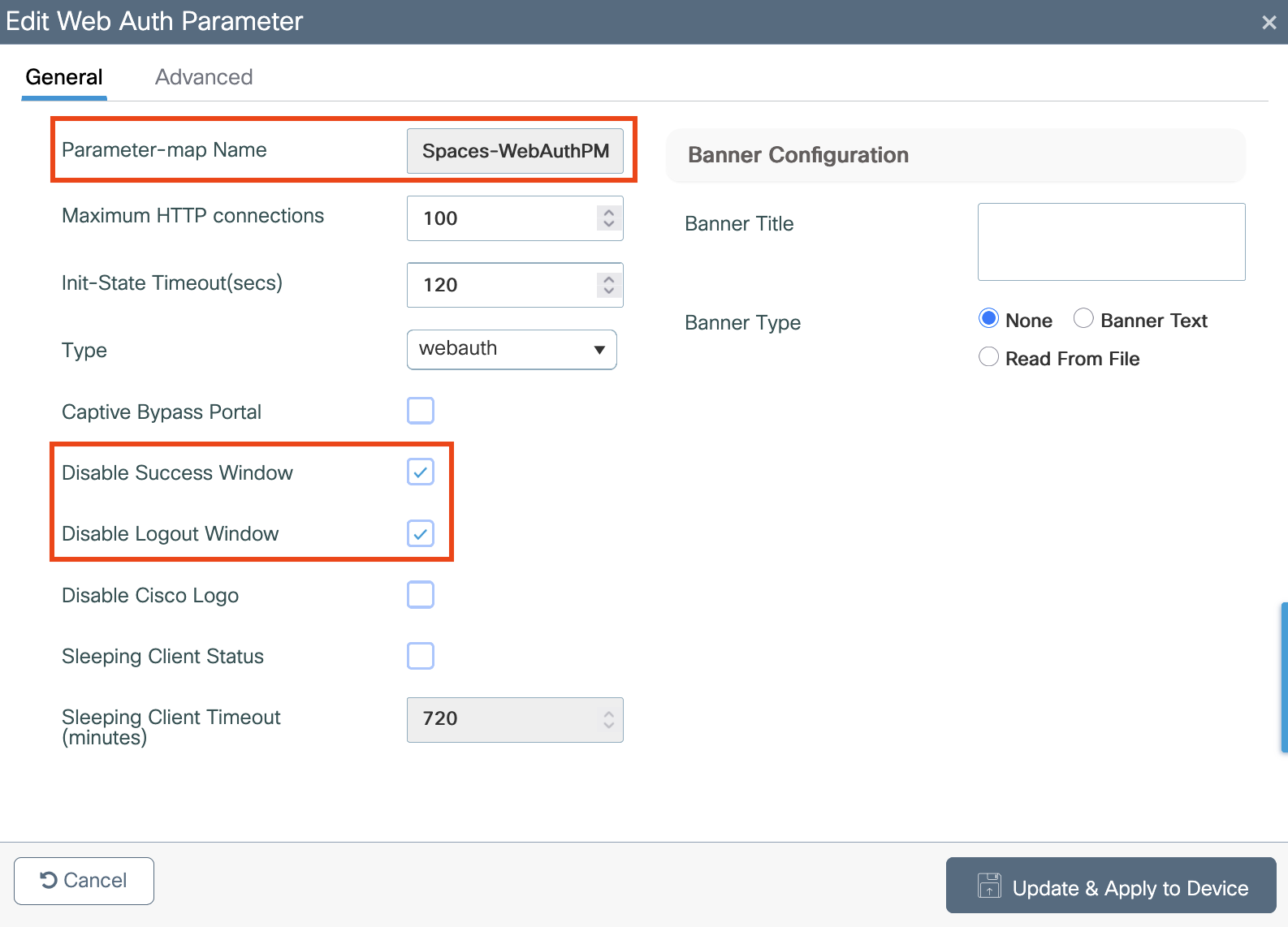
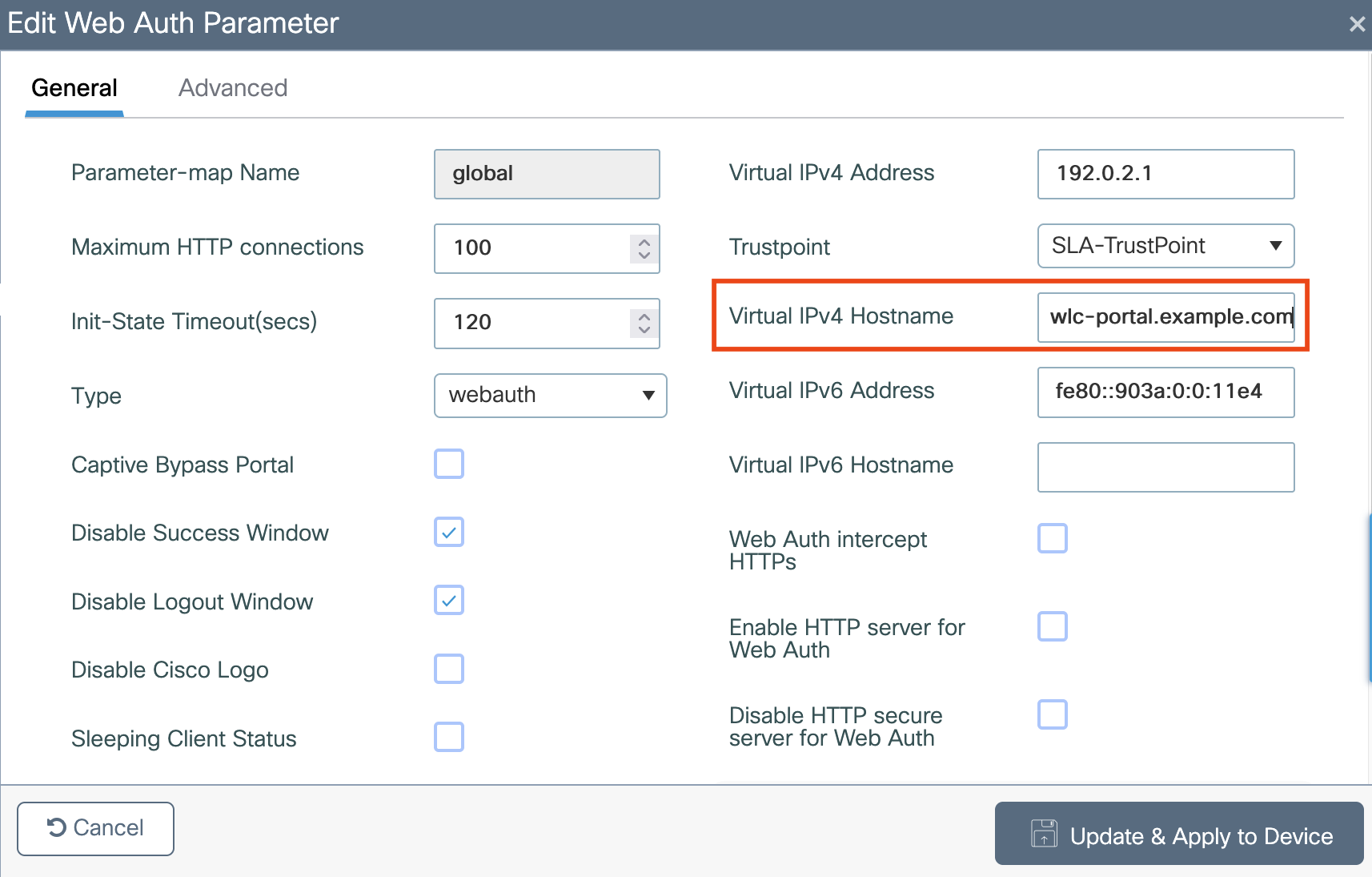
Log in to the Catalyst 9800 WLC web GUI
Navigate to Configuration > Security > Web Auth
Click the “global” Web Auth to begin configuration
Locate Virtual IPv4 Hostname
Enter your chosen domain name (e.g.,
wlc-portal.example.com)Click Update & Apply to Device
Alternatively, via CLI:
CLI Config |
|---|
config |
Update Internal DNS: On your internal (on-premises) DNS server, create a DNS record that resolves the domain name to the virtual IP address (
192.0.2.1).Obtain the Certificate: Request a certificate from a public CA with the chosen domain name in the SAN field—do not include the private IP address.
Install the Certificate: Upload and apply the certificate to the Catalyst 9800 controller.
This approach ensures clients see a trusted certificate when accessing the captive portal, while avoiding issues with CAs rejecting certificates that reference private IPs.
This workaround relies on all client devices using your internal DNS when connecting to the wireless network.
If devices use external DNS (e.g., 8.8.8.8), they may not be able to resolve the domain, potentially causing captive portal issues.
Always ensure the domain name used is not publicly resolvable to avoid conflicts or security concerns.
After changing the virtual IP DNS name, you may need to clear client browser DNS caches or disconnect/reconnect Wi-Fi clients for changes to take effect.